
1
CNSSI No. 1253
27 March 2014
SECURITY CATEGORIZATION AND
CONTROL SELECTION FOR
NATIONAL SECURITY SYSTEMS
THIS INSTRUCTION PRESCRIBES MINIMUM STANDARDS
YOUR DEPARTMENT OR AGENCY MAY REQUIRE FURTHER
IMPLEMENTATION

CNSSI No. 1253
i
NATIONAL MANAGER
FOREWORD
1. The Committee on National Security Systems (CNSS) Instruction No. 1253, Security
Categorization and Control Selection for National Security Systems, provides all Federal
Government departments, agencies, bureaus, and offices with guidance on the first two steps of
the Risk Management Framework (RMF), Categorize and Select, for national security systems
(NSS). This Instruction builds on and is a companion document to National Institute of
Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP), 800-53, Security and Privacy
Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations; therefore, it is formatted to align
with that document’s section numbering scheme. This Instruction should be used by information
systems security engineers, authorizing officials, senior information security officers, and others
to select and agree upon appropriate protections for an NSS.
2. The authority to issue this Instruction derives its authority from National Security Directive
42, National Policy for the Security of National Security Telecommunications and Information
Systems, which outlines the roles and responsibilities for securing NSS, consistent with
applicable law, E.O. 12333, as amended, and other Presidential directives. Nothing in this
Instruction shall alter or supersede the authorities of the Director of National Intelligence.
3. This Instruction supersedes CNSSI No. 1253 dated March 15, 2012.
4. All CNSS member organizations should plan their transition to new versions of this
Instruction, including periodic updates of the security control allocations. The transition should
account for new overlays that are published independently as attachments to Appendix F of this
Instruction.
5. CNSSI No. 1253 appendices will be reviewed and administratively updated, as required, on a
quarterly basis to reflect changes to protect NSS.
6. Additional copies of this Instruction may be obtained from the CNSS Secretariat or the CNSS
website: https://www.cnss.gov.
FOR THE NATIONAL MANAGER
/s/
DEBORA A. PLUNKETT
CNSS Secretariat (IE32). National Security Agency. 9800 Savage Road, STE 6716. Ft Meade, MD 20755-6716
Office: (410) 854-6805 Unclassified FAX: (410) 854-6814
CNSS@nsa.gov
CNSSI No. 1253
ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION ..........................................................................................1
1.1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE ...........................................................................................................1
1.2 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CNSSI NO. 1253 AND NIST PUBLICATIONS .....................2
CHAPTER TWO: THE FUNDAMENTALS ..............................................................................3
2.1 ADOPTION OF NIST SP 800-53 AND FIPS 199 ...................................................................3
2.2 ASSUMPTIONS RELATED TO SECURITY CONTROL BASELINES ..............................3
2.3 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BASELINES AND OVERLAYS ...........................................4
CHAPTER THREE: THE CATEGORIZE AND SELECT PROCESSES .............................5
3.1 RMF STEP 1: CATEGORIZE INFORMATION SYSTEM ...................................................5
3.2 RMF STEP 2: SELECT SECURITY CONTROLS ................................................................6
APPENDIX A REFERENCES ................................................................................................ A-1
APPENDIX B GLOSSARY ......................................................................................................B-1
APPENDIX C ACRONYMS ....................................................................................................C-1
APPENDIX D SECURITY CONTROL TABLES ................................................................ D-1
APPENDIX E SECURITY CONTROL PARAMETER VALUES ...................................... E-1
APPENDIX F OVERLAYS ...................................................................................................... F-1
TABLE OF FIGURES AND TABLES
Table D-1: NSS Security Control Baselines .............................................................................. D-1
Table D-2: Additional Security Control Information ............................................................... D-37
Table E-1: Security Control Parameter Values for NSS ............................................................. E-1

CNSSI No. 1253
1
CHAPTER ONE
INTRODUCTION
The CNSS has worked with representatives from the Civil, Defense, and Intelligence
Communities, as part of the Joint Task Force Transformation Initiative Working Group (JTF) to
produce a unified information security framework. As a result of this collaboration, NIST
published the following five transformational documents:
NIST SP 800-30, Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments;
NIST SP 800-37, Guide for Applying the Risk Management Framework to Federal
Information Systems: A Security Life Cycle Approach;
NIST SP 800-39, Managing Information Security Risk: Organization, Mission, and
Information System View;
NIST SP 800-53, Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and
Organizations; and
NIST SP 800-53A, Guide for Assessing the Security Controls in Federal Information
Systems and Organizations: Building Effective Security Assessment Plans.
The intent of this common framework is to improve information security, strengthen risk
management processes, and encourage reciprocity among federal agencies.
1.1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE
The CNSS collaborates with NIST to ensure NIST SP 800-53 contains security controls to meet
the requirements of NSS
1
and provides a common foundation for information security across the
U.S. Federal Government. CNSSI No. 1253 is a companion document to the NIST publications
relevant to categorization and selection (i.e., NIST SP 800-53; NIST SP 800-37; NIST SP 800-
60, Guide for Mapping Types of Information and Information Systems to Security Categories;
and Federal Information Processing Standards [FIPS] 199, Standards for Security Categorization
of Federal Information and Information Systems) and applies to all NSS. This Instruction also
provides NSS-specific information on developing and applying overlays for the national security
community and parameter values for NIST SP 800-53 security controls that are applicable to all
NSS.
For NSS, where differences between the NIST documentation and this Instruction occur, this
Instruction takes precedence.
1
NIST SP 800-59, Guidelines for Identifying an Information System as a National Security System, provides guidelines
developed in conjunction with the Department of Defense, including the National Security Agency, for identifying an
information system as a national security system. The basis for these guidelines is the Federal Information Security Management
Act of 2002 (Title III, Public Law 107-347, December 17, 2002), which defines the phrase “national security system,” and
provides government-wide requirements for information security.
CNSSI No. 1253
2
1.2 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CNSSI NO. 1253 AND NIST PUBLICATIONS
The major differences between this Instruction and the NIST publications relevant to
categorization and selection are below.
This Instruction does not adopt the high water mark (HWM) concept from FIPS 200,
Minimum Security Requirements for Federal Information and Information Systems, for
categorizing information systems (see Section 2.1).
The definitions for moderate and high impact are refined from those provided in FIPS
199 (see Section 3.1).
The associations of confidentiality, integrity, and/or availability to security controls are
explicitly defined in this Instruction (see Appendix D, Table D-2).
The use of security control overlays is refined in this Instruction for the national security
community (see Section 3.2 and Appendix F).

CNSSI No. 1253
3
CHAPTER TWO
THE FUNDAMENTALS
This chapter presents the fundamental concepts associated with categorization and security
control selection.
2.1 ADOPTION OF NIST SP 800-53 AND FIPS 199
The CNSS adopts NIST SP 800-53, as documented in this Instruction, for the national security
community. The CNSS adopts FIPS 199, establishing the security category for NSS with three
discrete components: one impact value (low, moderate, or high) for each of the three security
objectives (confidentiality, integrity, and availability). Preserving the three discrete components,
rather than using the FIPS 200 HWM, provides granularity in allocating security controls to
baselines and reduces the need for subsequent tailoring. Table D-1 in Appendix D represents
this in a 3-by-3 matrix.
2.2 ASSUMPTIONS RELATED TO SECURITY CONTROL BASELINES
Assumptions related to security control baselines are intended to represent a majority of federal
information systems and serve as the basis to justify the allocation of controls in the baselines.
While some federal information systems do not share these characteristics, it is more efficient for
organizations to start with a baseline and tailor it to meet the needs of those information systems.
Systems or environments that diverge from the assumptions listed below
2
may require the
application of an overlay (see Section 3.2.1) or tailoring of the selected controls and
enhancements (see Section 3.2.2).
This Instruction accepts all assumptions from NIST SP 800-53 by adopting the NIST security
control baselines as the foundation for the NSS baselines defined in Table D-1, in Appendix D.
The NIST SP 800-53 assumptions are:
Information systems are located in physical facilities.
User data/information in organizational information systems is relatively persistent.
Information systems are multi-user (either serially or concurrently) in operation.
Some user data/information in organizational information systems is not shareable with
other users who have authorized access to the same systems.
Information systems exist in networked environments.
Information systems are general purpose in nature.
Organizations have the structure, resources, and infrastructure to implement the controls.
This Instruction also addresses assumptions specific to NSS through the NSS baselines. The
NSS baselines are not intended to address these assumptions completely, but rather to a degree
that represents the minimal protection that should be provided. The additional, NSS-specific
assumptions are:
2
Examples of systems that may diverge from the assumptions include systems not located in physical facilities, systems in
resource constrained environments, and stand-alone systems.

CNSSI No. 1253
4
Insider threats exist within NSS organizations.
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are targeting NSS and may already exist within NSS
organizations.
Additional best practices beyond those defined in the NIST baselines are necessary to
protect NSS.
Conversely, there are also some possible situations that are specifically not addressed in the
baselines. These include:
Classified data/information is processed, stored, or transmitted by information systems;
Selected data/information requires specialized protection based on federal legislation,
directives, regulations, or policies; and
Information systems need to communicate with other systems across different security
domains.
2.3 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BASELINES AND OVERLAYS
NSS baselines, which are comprised of NIST SP 800-53 baselines coupled with the additional
NIST SP 800-53 security controls required for NSS, and applicable overlays together constitute
the initial security control set. NSS baselines represent the security controls necessary to address
the impact on organizations or individuals should there be a loss of confidentiality, integrity, or
availability, as reflected by the system’s security category. Overlays are intended to address
additional factors (beyond impact) or diverge from the assumptions used to create the security
control baselines (see Section 2.2), the use of which is determined by answering the applicability
questions in each overlay.
Overlays are baseline independent, meaning that they can be applied to any NSS baseline (e.g.,
High-Moderate-Moderate or Low-Low-Low). As a result, there may be overlap of security
controls between an NSS baseline and security controls identified in an overlay(s).
3
Together,
the combination of an NSS baseline and applicable overlay(s) represents the initial security
control set prior to system-specific tailoring.
All security controls, regardless of source (baseline or overlays), may be tailored to address the
risk associated with the specific system. All security controls, whether from a baseline or an
overlay, are implemented in a system and tested during the security control assessment process.
3
If the use of multiple overlays results in conflicts between the application and removal of security controls, see Section 3.2.1 for
guidance.

CNSSI No. 1253
5
CHAPTER THREE
THE CATEGORIZE AND SELECT PROCESSES
This chapter describes the processes of categorization and security control selection. Except
where the guidance in this document differs from that in NIST SP 800-37, the national security
community will implement the RMF Categorize and Select Steps consistent with NIST SP 800-
37.
3.1 RMF STEP 1: CATEGORIZE INFORMATION SYSTEM
For NSS, the Security Categorization Task (RMF Step 1, Task 1-1) is a two-step process:
1. Determine impact values: (i) for the information type(s)
4
processed, stored, transmitted,
or protected
5
by the information system; and (ii) for the information system.
2. Identify overlays that apply to the information system and its operating environment to
account for additional factors (beyond impact) that influence the selection of security
controls.
Within the national security community, it is understood that certain losses are to be expected
when performing particular missions. Therefore, for NSS interpret the FIPS 199 amplification
for the moderate and high potential impact values, as if the phrase “…exceeding mission
expectations.” is appended to the end of the sentence in FIPS 199, Section 3.
3.1.1 Determine Impact Values for Information Types and the Information System
In preparation for selecting and specifying the appropriate security controls for organizational
information systems and their respective environments of operation, organizations categorize
their information and information system. To categorize the information and information
system, complete the following activities:
1. Identify all the types of information processed, stored, or transmitted by an information
system, determine their provisional security impact values, and adjust the information
types’ provisional security impact values (see FIPS 199, NIST SP 800-60, Volume I,
Section 4, and NIST SP 800-60, Volume II)
6
. If the information type is not identified in
NIST SP 800-60 Volume II, document the information type consistent with the guidance
in NIST SP 800-60, Volume I.
7
2. Determine the security category for the information system (see FIPS 199) and make any
necessary adjustments (see NIST SP 800-60, Volume I, Section 4.4.2). The security
category of a system should not be changed or modified to reflect management decisions
4
An information type is a specific category of information (e.g., privacy, medical, proprietary, financial, investigative,
contractor-sensitive, security management), defined by an organization or, in some instances, by a public law, executive order,
directive, policy, or regulation.
5
Controlled interfaces protect information that is processed, stored, or transmitted on interconnected systems. That information
should be considered when categorizing the controlled interface.
6
For the confidentiality impact value, each organization should ensure that it categorizes specific information based on its
potential worst case impact to i) its organization and ii) any and all other U.S. organizations with that specific information.
7
As appropriate, supplement NIST SP 800-60 with organization-defined guidance.
CNSSI No. 1253
6
to allocate more stringent or less stringent security controls. The tailoring guidance in
Section 3.2.2 should be used to address these issues.
3. Document the security category in the security plan.
3.1.2 Identify Applicable Overlays
Overlays identify additional factors (beyond impact) that influence the initial selection of
security controls. As CNSS overlays are developed, they are published as attachments to
Appendix F of this Instruction. Each overlay includes an applicability section with a series of
questions used to identify whether or not the overlay is applicable to an information system.
Review the questions in each overlay identified in Appendix F to determine whether or not the
overlay applies. Document the applicable overlay(s) in the security plan.
3.2 RMF STEP 2: SELECT SECURITY CONTROLS
For NSS, Security Control Selection (RMF Step 2, Task 2-2) is a two-step process:
1. Select the initial security control set.
2. Tailor the initial security control set.
3.2.1 Select the Initial Security Control Set
Once the security category of the information system is determined, organizations begin the
security control selection process. To identify the initial security control set, complete the
following activities:
1. Select the baseline security controls identified from Table D-1 in Appendix D
corresponding to the security category of the system (i.e., the impact values determined
for each security objective [confidentiality, integrity, and availability]).
2. Apply any overlay(s) identified as applicable during security categorization. If the use of
multiple overlays results in conflicts between the application or removal of security
controls, the authorizing official (or designee), in coordination with the information
owner/steward, information system owner, and risk executive (function) resolves the
conflict.
3. Document the initial security control set and the rationale for adding or removing security
controls from the baseline by referencing the applicable overlay(s) in the security plan.
3.2.2 Tailor the Initial Security Control Set
Organizations initiate the tailoring process to modify and align the initial control set to more
closely account for conditions affecting the specific system (i.e., conditions related to
organizational missions/business functions, information systems, or environments of operation).
Organizations should remove security controls only as a function of specified, risk-based
determinations. During the tailoring process, a risk assessment – either informal or formal –
should be conducted. The results from a risk assessment provide information about the necessity

CNSSI No. 1253
7
and sufficiency of security controls and enhancements during the tailoring process. To tailor the
initial security control set, complete the following activities:
1. Tailor the initial security control set using Table D-2, Appendix E, and NIST SP 800-53,
Section 3.2.
8
2. Determine whether or not additional assurance–related controls are needed to increase the
level of trustworthiness in the information system. If so, tailor the set of controls
accordingly. (See NIST SP 800-53, Appendix E.)
3. Document in the security plan the relevant decisions made during the tailoring process,
providing a sound rationale for those decisions.
4. Document and justify in the security plan any security controls from the initial security
control set that cannot or will not be implemented in the system and for which no
compensating control(s) will be substituted. At the discretion of the authorizing official,
this information may be included in the plan of action and milestones.
8
All of the guidance in NIST SP 800-53, Section 3.2 applies to NSS except for the subsection titled “Security Objective-Related
Considerations.” This subsection is specific to the NIST baselines and does not apply to NSS.

CNSSI No. 1253
A-1
APPENDIX A
REFERENCES
LAWS, POLICIES, DIRECTIVES, REGULATIONS, MEMORANDA, STANDARDS, AND
GUIDELINES
Appendix A provides the references used within CNSSI No. 1253.
1. 44 U.S.C. § 3542, January 2012.
2. Committee on National Security Systems Instruction 4009, National Information
Assurance Glossary, April 2010.
3. Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 199, Standards for Security
Categorization of Federal Information and Information Systems, February 2004.
4. Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 200, Minimum Security
Requirements for Federal Information and Information Systems, March 2006.
5. Federal Information Security Management Act (P.L. 107-347, Title III), December 2002.
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-30, Guide for
Conducting Risk Assessments, September 2012.
7. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-37, Revision 1,
Guide for Applying the Risk Management Framework to Federal Information Systems: A
Security Life Cycle Approach, February 2010.
8. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-39, Managing
Information Security Risk: Organization, Mission, and Information System View, March
2011.
9. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-53, Revision 4,
Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations, April
2013.
9
10. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-53A, Guide for
Assessing the Security Controls in Federal Information Systems and Organizations:
Building Effective Security Assessment Plans, June 2010.
11. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-59, Guideline for
Identifying an Information System as a National Security System, August 2003.
12. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-60, Revision 1,
Volume I: Guide for Mapping Types of Information and Information Systems to Security
Categories, August 2008.
13. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-60, Revision 1,
Volume II: Appendices to Guide for Mapping Types of Information and Information
Systems to Security Categories, August 2008
14. National Security Directive 42, National Policy for the Security of National Security
Telecommunications and Information Systems, July 1990.
9
Includes errata update as of 7 May 2013.

CNSSI No. 1253
B-1
APPENDIX B
GLOSSARY
COMMON TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
The terms in this document are defined in the NIST JTF documents and CNSSI No. 4009, except
for those listed below.
Initial Security Control Set
The set of security controls resulting from the combination of a
baseline and applicable overlays prior to system specific tailoring.
NSS baselines
The combination of NIST 800-53 baselines (represented by an
“X”) and the additional NIST SP 800-53 security controls required
for NSS (represented by a “+”) that are applicable to NSS.
Provisional security impact
values
[NIST SP 800-60,
Adapted]
The initial or conditional impact determinations made until all
considerations are fully reviewed, analyzed, and accepted in the
subsequent categorization steps by appropriate officials.
Security Control Extension
A statement, used in security control overlays, that extends the
basic capability of a security control by specifying additional
functionality, altering the strength mechanism, or adding or
limiting implementation options.
CNSSI No. 1253
C-1
APPENDIX C
ACRONYMS
COMMON ABBREVIATIONS
The acronyms and abbreviations used in this Instruction are included below. Control related
acronyms included in the tables of appendices D and E are defined in NIST SP 800-53.
APT
Advanced Persistent Threat
CNSS
Committee on National Security Systems
CNSSI
Committee on National Security Systems Instruction
EO
Executive Order
FIPS
Federal Information Processing Standards
FISMA
Federal Information Security Management Act
HWM
High Water Mark
JTF
Joint Task Force Transformation Initiative Working Group
NIST
National Institute of Standards and Technology
NSS
National Security System
RMF
Risk Management Framework
P.L.
Public Law
SC
Security Category
SDLC
System Development Life Cycle
SP
Special Publication
U.S.
United States
U.S.C.
United States Code

CNSSI No. 1253
D-1
APPENDIX D
SECURITY CONTROL TABLES
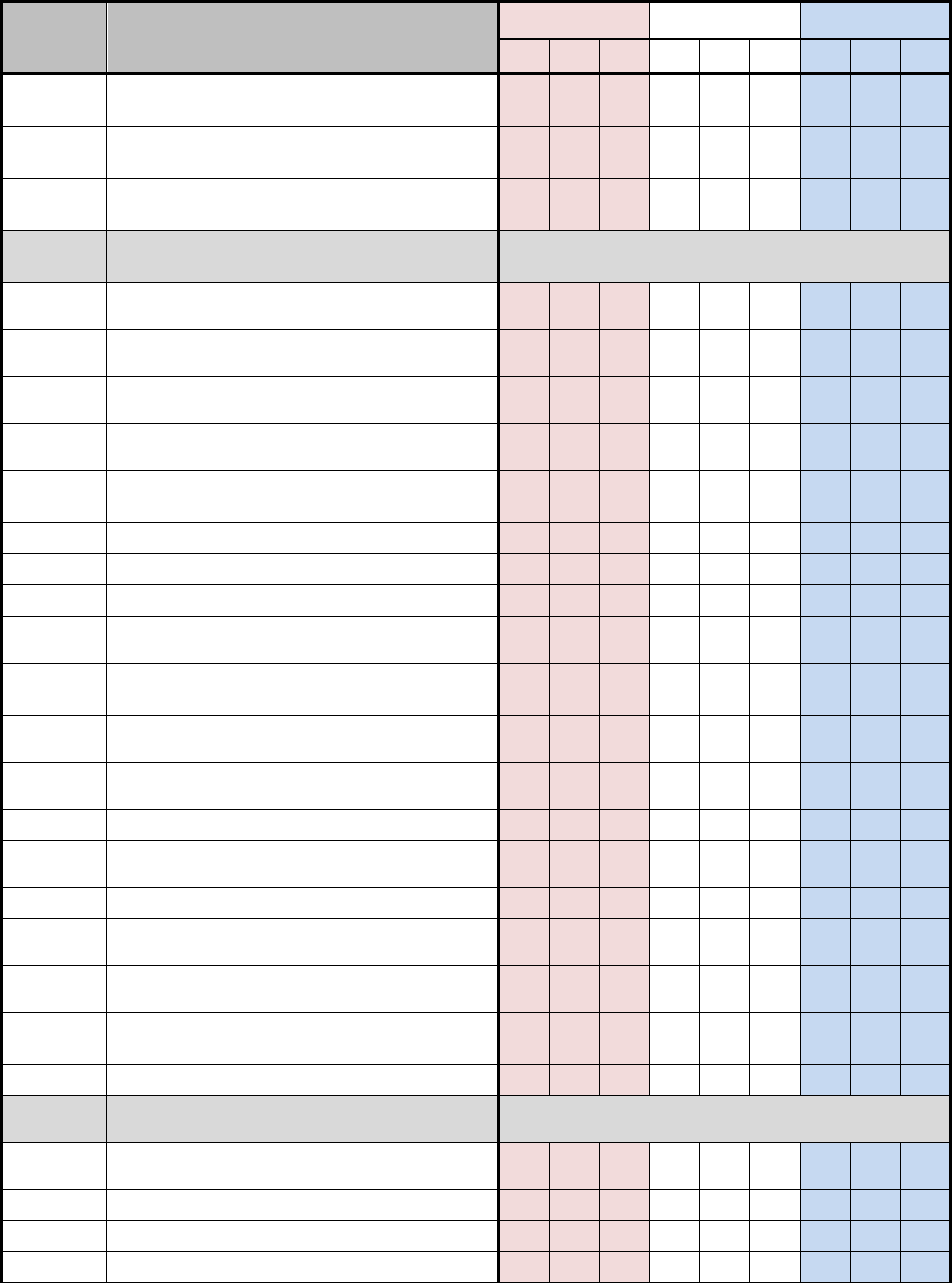
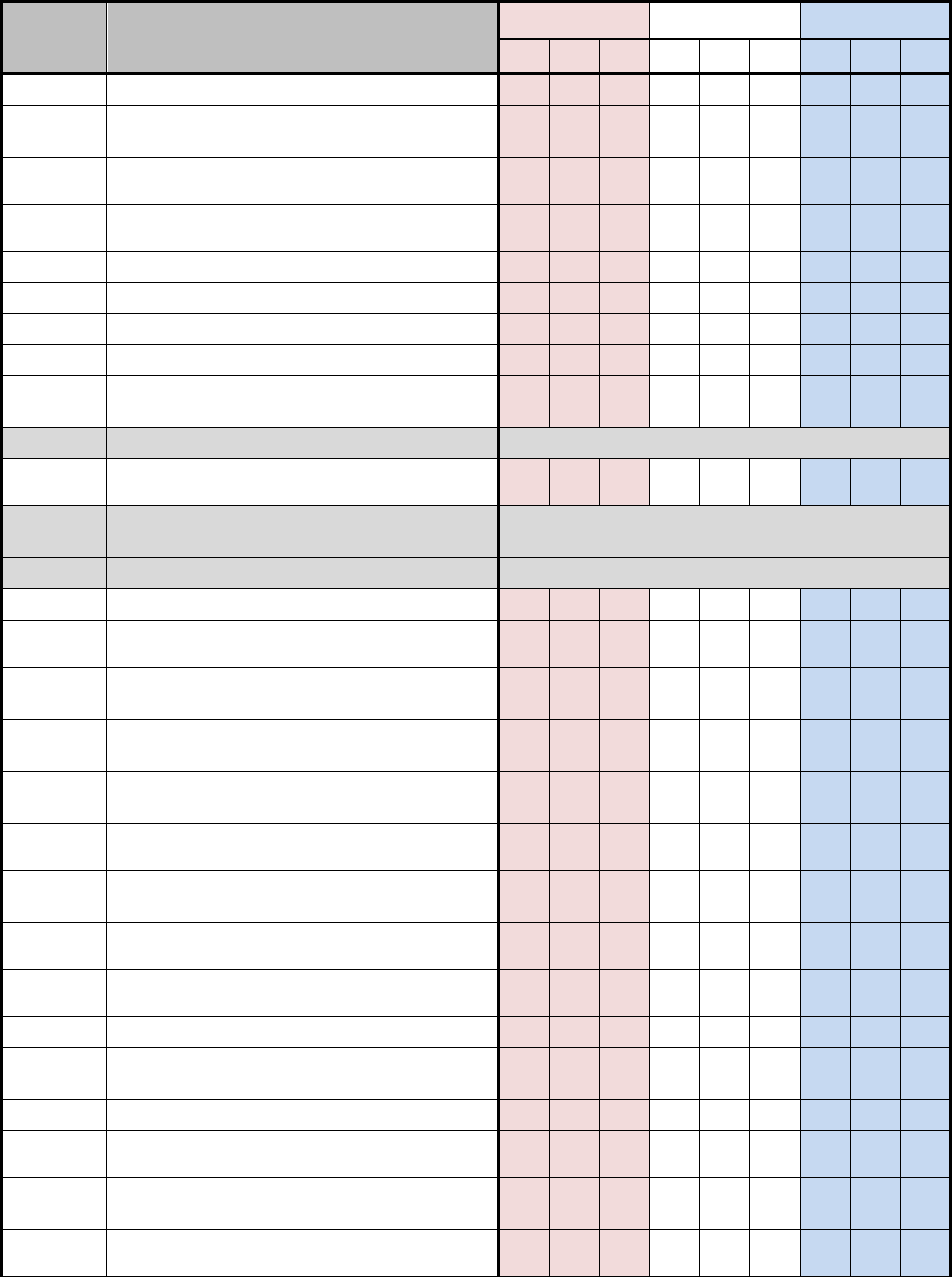
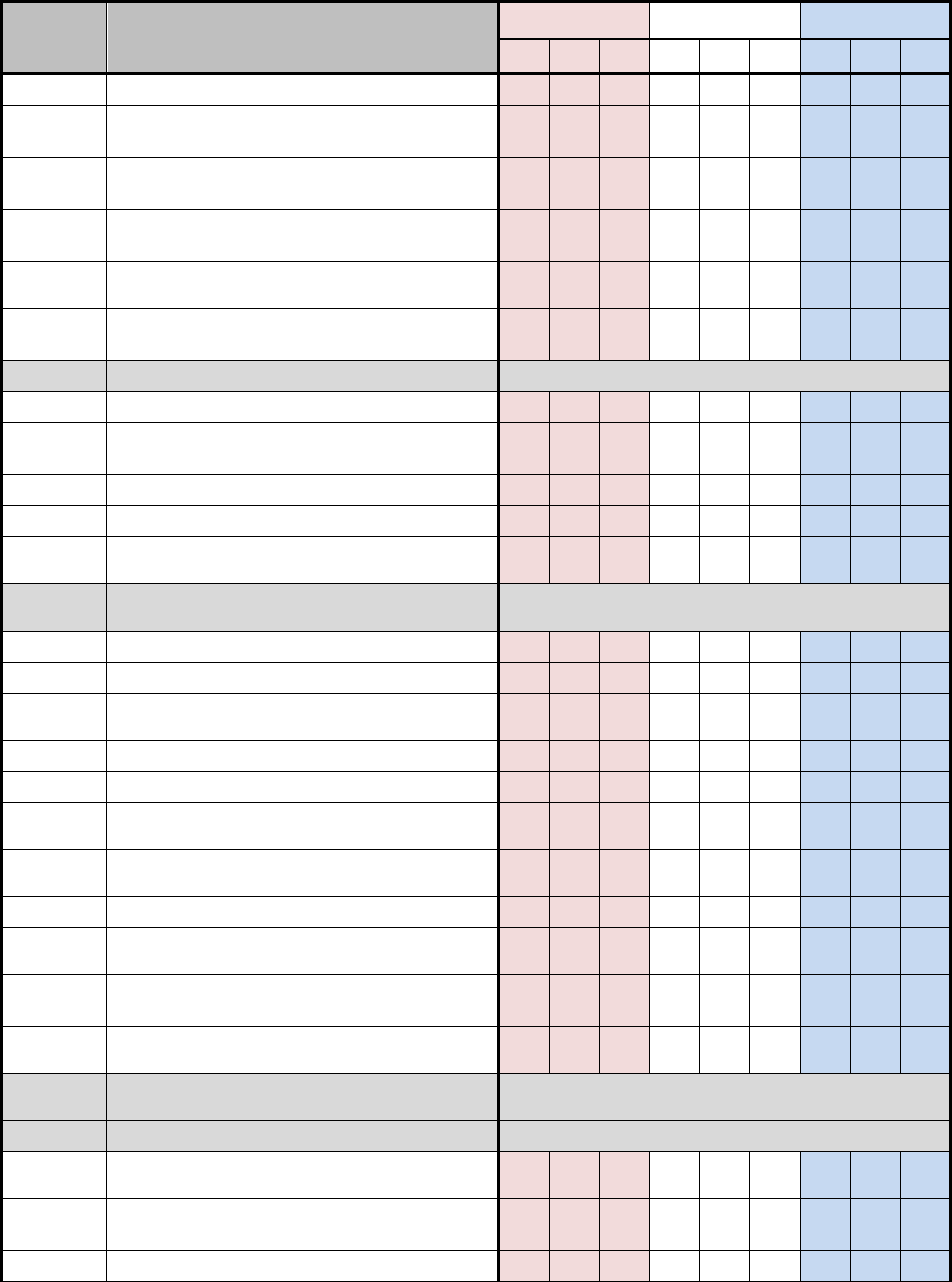
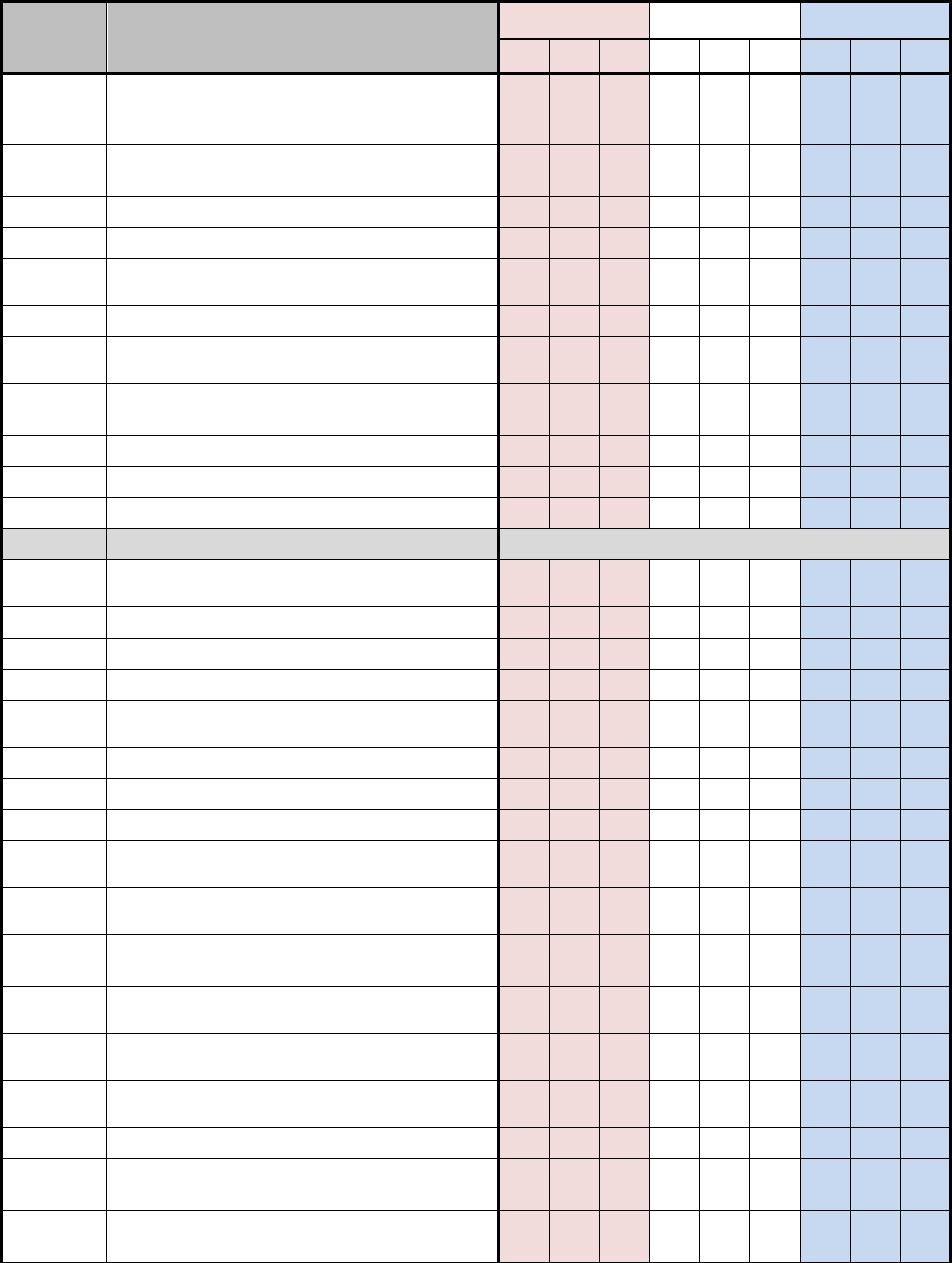
D.1 NSS SECURITY CONTROL BASELINES
Table D-1 uses a 3-by-3 matrix to identify applicability of security controls in the NIST SP 800-
53, Revision 4 baselines for NSS. The matrix also identifies the additional security controls
needed to protect NSS. This table represents the security controls applicable to NSS based on
impact values.
The 3-by-3 matrix has nine columns showing three possible impact values (low, moderate, or
high) for each of the three security objectives (confidentiality, integrity, or availability). The
"X"s in the table reflect the NIST specifications by impact value (i.e., low, moderate, and high).
The "+"s in the table reflect the additional CNSS specifications by impact value for all NSS. The
association of security controls to security objectives is detailed in table D-2. A blank space in
the table signifies the control was either not selected or not allocated to a particular security
objective for the purposes of this Instruction. Controls that are designated as “withdrawn”
indicate that they are no longer in the NIST SP 800-53 security control catalog
10
.
Table D-1: NSS Security Control Baselines
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
AC-1
Access Control Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-2
Account Management
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-2(1)
Account Management | Automated System
Account Management
X
X
X
X
AC-2(2)
Account Management | Removal of
Temporary / Emergency Accounts
X
X
X
X
AC-2(3)
Account Management | Disable Inactive
Accounts
X
X
X
X
AC-2(4)
Account Management | Automated Audit
Actions
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-2(5)
Account Management | Inactivity Logout
+
+
X
+
+
X
+
+
X
AC-2(6)
Account Management | Dynamic Privilege
Management
AC-2(7)
Account Management | Role-Based Schemes
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-2(8)
Account Management | Dynamic Account
Creation
AC-2(9)
Account Management | Restrictions on Use of
Shared Groups / Accounts
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-2(10)
Account Management | Shared / Group
Account Credential Termination
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-2(11)
Account Management | Usage Conditions
X
X
AC-2(12)
Account Management | Account Monitoring /
+
+
X
+
+
X
10
Changes to the security control catalog are under the authority of NIST.

CNSSI No. 1253
D-2
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Atypical Usage
AC-2(13)
Account Management | Disable Accounts For
High-Risk Individuals
+
+
X
+
+
X
AC-3
Access Enforcement
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-3(1)
Access Enforcement | Restricted Access to
Privileged Functions
Withdrawn
AC-3(2)
Access Enforcement | Dual Authorization
AC-3(3)
Access Enforcement | Mandatory Access
Control
AC-3(4)
Access Enforcement | Discretionary Access
Control
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-3(5)
Access Enforcement | Security-Relevant
Information
AC-3(6)
Access Enforcement | Protection of User and
System Information
Withdrawn
AC-3(7)
Access Enforcement | Role-Based Access
Control
AC-3(8)
Access Enforcement | Revocation of Access
Authorizations
AC-3(9)
Access Enforcement | Controlled Release
AC-3(10)
Access Enforcement | Audited Override of
Access Control Mechanisms
AC-4
Information Flow Enforcement
X
X
X
X
AC-4(1)
Information Flow Enforcement | Object
Security Attributes
AC-4(2)
Information Flow Enforcement | Processing
Domains
AC-4(3)
Information Flow Enforcement | Dynamic
Information Flow Control
AC-4(4)
Information Flow Enforcement | Content
Check Encrypted Information
AC-4(5)
Information Flow Enforcement | Embedded
Data Types
AC-4(6)
Information Flow Enforcement | Metadata
AC-4(7)
Information Flow Enforcement | One-Way
Flow Mechanisms
AC-4(8)
Information Flow Enforcement | Security
Policy Filters
AC-4(9)
Information Flow Enforcement | Human
Reviews
AC-4(10)
Information Flow Enforcement | Enable /
Disable Security Policy Filters
AC-4(11)
Information Flow Enforcement |
Configuration of Security Policy Filters
AC-4(12)
Information Flow Enforcement | Data Type
Identifiers
AC-4(13)
Information Flow Enforcement |
Decomposition Into Policy-Relevant
CNSSI No. 1253
D-3
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Subcomponents
AC-4(14)
Information Flow Enforcement | Security
Policy Filter Constraints
AC-4(15)
Information Flow Enforcement | Detection of
Unsanctioned Information
AC-4(16)
Information Flow Enforcement | Information
Transfers on Interconnected Systems
Withdrawn
AC-4(17)
Information Flow Enforcement | Domain
Authentication
AC-4(18)
Information Flow Enforcement | Security
Attribute Binding
AC-4(19)
Information Flow Enforcement | Validation
of Metadata
AC-4(20)
Information Flow Enforcement | Approved
Solutions
AC-4(21)
Information Flow Enforcement | Physical /
Logical Separation of Information Flows
AC-4(22)
Information Flow Enforcement | Access Only
AC-5
Separation of Duties
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-6
Least Privilege
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-6(1)
Least Privilege | Authorize Access to Security
Functions
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-6(2)
Least Privilege | Non-Privileged Access For
Nonsecurity Functions
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-6(3)
Least Privilege | Network Access to
Privileged Commands
X
X
AC-6(4)
Least Privilege | Separate Processing
Domains
AC-6(5)
Least Privilege | Privileged Accounts
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-6(6)
Least Privilege | Privileged Access by Non-
Organizational Users
AC-6(7)
Least Privilege | Review of User Privileges
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-6(8)
Least Privilege | Privilege Levels For Code
Execution
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-6(9)
Least Privilege | Auditing Use of Privileged
Functions
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-6(10)
Least Privilege | Prohibit Nonprivileged
Users from Executing Privileged Functions
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-7
Unsuccessful Logon Attempts
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-7(1)
Unsuccessful Logon Attempts | Automatic
Account Lock
Withdrawn
AC-7(2)
Unsuccessful Logon Attempts | Purge/Wipe
Mobile Device
AC-8
System Use Notification
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-9
Previous Logon (Access) Notification
AC-9(1)
Previous Logon Notification | Unsuccessful
CNSSI No. 1253
D-4
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Logons
AC-9(2)
Previous Logon Notification | Successful /
Unsuccessful Logons
AC-9(3)
Previous Logon Notification | Notification of
Account Changes
AC-9(4)
Previous Logon Notification | Additional
Logon Information
AC-10
Concurrent Session Control
+
X
+
X
+
X
AC-11
Session Lock
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-11(1)
Session Lock | Pattern-Hiding Displays
+
X
X
AC-12
Session Termination
X
X
X
X
AC-12(1)
Session Termination | User-initiated Logouts
/ Message Displays
+
+
+
+
AC-13
Supervision and Review — Access Control
Withdrawn
AC-14
Permitted Actions Without Identification or
Authentication
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-14(1)
Permitted Actions Without Identification or
Authentication | Necessary Uses
Withdrawn
AC-15
Automated Marking
Withdrawn
AC-16
Security Attributes
+
+
+
+
AC-16(1)
Security Attributes | Dynamic Attribute
Association
AC-16(2)
Security Attributes | Attribute Value Changes
by Authorized Individuals
AC-16(3)
Security Attributes | Maintenance of Attribute
Associations by Information System
AC-16(4)
Security Attributes | Association of Attributes
by Authorized Individuals
AC-16(5)
Security Attributes | Attribute Displays For
Output Devices
AC-16(6)
Security Attributes | Maintenance of Attribute
Association by Organization
+
+
+
+
AC-16(7)
Security Attributes | Consistent Attribute
Interpretation
AC-16(8)
Security Attributes | Association Techniques /
Technologies
AC-16(9)
Security Attributes | Attribute Reassignment
AC-
16(10)
Security Attributes | Attribute Configuration
by Authorized Individuals
AC-17
Remote Access
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-17(1)
Remote Access | Automated Monitoring /
Control
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-17(2)
Remote Access | Protection of Confidentiality
/ Integrity Using Encryption
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-17(3)
Remote Access | Managed Access Control
Points
+
X
X
+
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-5
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
AC-17(4)
Remote Access | Privileged Commands /
Access
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-17(5)
Remote Access | Monitoring For
Unauthorized Connections
Withdrawn
AC-17(6)
Remote Access | Protection of Information
+
+
+
AC-17(7)
Remote Access | Additional Protection For
Security Function Access
Withdrawn
AC-17(8)
Remote Access | Disable Nonsecure Network
Protocols
Withdrawn
AC-17(9)
Remote Access | Disconnect / Disable Access
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-18
Wireless Access
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-18(1)
Wireless Access | Authentication and
Encryption
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-18(2)
Wireless Access | Monitoring Unauthorized
Connections
Withdrawn
AC-18(3)
Wireless Access | Disable Wireless
Networking
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-18(4)
Wireless Access | Restrict Configurations by
Users
+
+
X
+
+
X
AC-18(5)
Wireless Access | Antennas / Transmission
Power Levels
X
X
AC-19
Access Control For Mobile Devices
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-19(1)
Access Control For Mobile Devices | Use of
Writable / Portable Storage Devices
Withdrawn
AC-19(2)
Access Control For Mobile Devices | Use of
Personally Owned Portable Storage Devices
Withdrawn
AC-19(3)
Access Control For Mobile Devices | Use of
Portable Storage Devices with No
Identifiable Owner
Withdrawn
AC-19(4)
Access Control For Mobile Devices |
Restrictions For Classified Information
AC-19(5)
Access Control For Mobile Devices | Full
Device / Container-Based Encryption
X
X
X
X
AC-20
Use of External Information Systems
X
X
X
X
X
X
AC-20(1)
Use of External Information Systems | Limits
on Authorized Use
+
X
X
+
X
X
AC-20(2)
Use of External Information Systems |
Portable Storage Devices
+
X
X
AC-20(3)
Use of External Information Systems | Non-
Organizationally Owned Systems / /
Components / Devices
+
+
+
+
+
+
AC-20(4)
Use of External Information Systems |
Network Accessible Storage Devices
AC-21
Information Sharing
X
X
AC-21(1)
Information Sharing | Automated Decision
Support
AC-21(2)
Information Sharing | Information Search and
Retrieval

CNSSI No. 1253
D-6
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
AC-22
Publicly Accessible Content
X
X
X
AC-23
Data Mining Protection
+
+
AC-24
Access Control Decisions
AC-24(1)
Access Control Decisions | Transmit Access
Authorization Information
AC-24(2)
Access Control Decisions | No User or
Process Identity
AC-25
Reference Monitor
AT-1
Security Awareness and Training Policy and
Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AT-2
Security Awareness Training
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AT-2(1)
Security Awareness | Practical Exercises
AT-2(2)
Security Awareness | Insider Threat
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
AT-3
Role-Based Security Training
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AT-3(1)
Security Training | Environmental Controls
AT-3(2)
Security Training | Physical Security Controls
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
AT-3(3)
Security Training | Practical Exercises
AT-3(4)
Security Training | Suspicious
Communications and Anomalous System
Behavior
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
AT-4
Security Training Records
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AT-5
Contacts With Security Groups and
Associations
Withdrawn
AU-1
Audit and Accountability Policy and
Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AU-2
Audit Events
X
X
X
X
X
X
AU-2(1)
Audit Events | Compilation of Audit Records
From Multiple Sources
Withdrawn
AU-2(2)
Audit Events | Selection of Audit Events by
Component
Withdrawn
AU-2(3)
Audit Events | Reviews and Updates
+
X
X
+
X
X
AU-2(4)
Audit Events | Privileged Functions
Withdrawn
AU-3
Content of Audit Records
X
X
X
X
X
X
AU-3(1)
Content of Audit Records | Additional Audit
Information
+
X
X
+
X
X
AU-3(2)
Content of Audit Records | Centralized
Management of Planned Audit Record
Content
X
X
AU-4
Audit Storage Capacity
X
X
X
AU-4(1)
Audit Storage Capacity | Transfer to Alternate
Storage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
AU-5
Response to Audit Processing Failures
X
X
X
AU-5(1)
Response to Audit Processing Failures | Audit
Storage Capacity
+
+
X
AU-5(2)
Response to Audit Processing Failures | Real-
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-7
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Time Alerts
AU-5(3)
Response to Audit Processing Failures |
Configurable Traffic Volume Thresholds
AU-5(4)
Response to Audit Processing Failures |
Shutdown on Failure
AU-6
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting
X
X
X
X
X
X
AU-6(1)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Process Integration
+
X
X
+
X
X
AU-6(2)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Automated Security Alerts
Withdrawn
AU-6(3)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Correlate Audit Repositories
+
X
X
+
X
X
AU-6(4)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Central Review and Analysis
+
+
+
+
+
+
AU-6(5)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Integration / Scanning and Monitoring
Capabilities
X
X
AU-6(6)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Correlation With Physical Monitoring
X
X
AU-6(7)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Permitted Actions
AU-6(8)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting | Full
Text Analysis of Privileged Commands
AU-6(9)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Correlation with Information from
Nontechnical Sources
AU-6(10)
Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting |
Audit Level Adjustment
+
+
+
+
+
+
AU-7
Audit Reduction and Report Generation
X
X
X
X
AU-7(1)
Audit Reduction and Report Generation |
Automatic Processing
X
X
X
X
AU-7(2)
Audit Reduction and Report Generation |
Automatic Sort and Search
AU-8
Time Stamps
X
X
X
AU-8(1)
Time Stamps | Synchronization With
Authoritative Time Source
+
X
X
AU-8(2)
Time Stamps | Secondary Authoritative Time
Source
AU-9
Protection of Audit Information
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
AU-9(1)
Protection of Audit Information | Hardware
Write-Once Media
AU-9(2)
Protection of Audit Information | Audit
Backup on Separate Physical Systems /
Components
X
AU-9(3)
Protection of Audit Information |
Cryptographic Protection
X
AU-9(4)
Protection of Audit Information | Access by
Subset of Privileged Users
+
X
X
+
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-8
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
AU-9(5)
Protection of Audit Information | Dual
Authorization
AU-9(6)
Protection of Audit Information | Read Only
Access
AU-10
Non-Repudiation
+
X
AU-10(1)
Non-Repudiation | Association of Identities
AU-10(2)
Non-Repudiation | Validate Binding of
Information Producer Identity
AU-10(3)
Non-Repudiation | Chain of Custody
AU-10(4)
Non-Repudiation | Validate Binding of
Information Reviewer Identity
AU-10(5)
Non-Repudiation | Digital Signatures
Withdrawn
AU-11
Audit Record Retention
X
X
X
AU-11(1)
Audit Record Retention | Long-Term
Retrieval Capability
+
+
+
AU-12
Audit Generation
X
X
X
X
X
X
AU-12(1)
Audit Generation | System-Wide / Time-
Correlated Audit Trail
+
+
X
AU-12(2)
Audit Generation | Standardized Formats
AU-12(3)
Audit Generation | Changes by Authorized
Individuals
+
+
X
+
+
X
AU-13
Monitoring For Information Disclosure
AU-13(1)
Monitoring For Information Disclosure | Use
of Automated Tools
AU-13(2)
Monitoring For Information Disclosure |
Review of Monitored Sites
AU-14
Session Audit
+
+
+
+
+
+
AU-14(1)
Session Audit | System Start-Up
+
+
+
+
+
+
AU-14(2)
Session Audit | Capture/Record and Log
Content
+
+
+
+
+
+
AU-14(3)
Session Audit | Remote Viewing / Listening
+
+
+
AU-15
Alternate Audit Capability
AU-16
Cross-Organizational Auditing
AU-16(1)
Cross-Organizational Auditing | Identity
Preservation
AU-16(2)
Cross-Organizational Auditing | Sharing of
Audit Information
CA-1
Security Assessment and Authorization
Policies and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-2
Security Assessments
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-2(1)
Security Assessments | Independent
Assessors
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
CA-2(2)
Security Assessments | Specialized
Assessments
X
X
X
CA-2(3)
Security Assessments | External
Organizations
CNSSI No. 1253
D-9
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
CA-3
System Interconnections
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-3(1)
System Interconnections | Unclassified
National Security System Connections
+
+
+
CA-3(2)
System Interconnections | Classified National
Security System Connections
CA-3(3)
System Interconnections | Unclassified Non-
National Security System Connections
CA-3(4)
System Interconnections | Connections to
Public Networks
CA-3(5)
System Interconnections | Restrictions on
External Network Connections
+
X
X
+
X
X
CA-4
Security Certification
Withdrawn
CA-5
Plan of Action and Milestones
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-5(1)
Plan of Action and Milestones | Automation
Support For Accuracy / Currency
CA-6
Security Authorization
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-7
Continuous Monitoring
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-7(1)
Continuous Monitoring | Independent
Assessment
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-7(2)
Continuous Monitoring | Types of
Assessments
Withdrawn
CA-7(3)
Continuous Monitoring | Trend Analyses
CA-8
Penetration Testing
X
CA-8(1)
Penetration Testing | Independent Penetration
Agent or Team
CA-8(2)
Penetration Testing | Red Team Exercises
CA-9
Internal System Connections
X
X
X
X
X
X
CA-9(1)
Internal System Connections | Security
Compliance Checks
CM-1
Configuration Management Policy and
Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
CM-2
Baseline Configuration
X
X
X
CM-2(1)
Baseline Configuration | Reviews and
Updates
+
X
X
CM-2(2)
Baseline Configuration | Automation Support
For Accuracy / Currency
X
CM-2(3)
Baseline Configuration | Retention of
Previous Configurations
X
X
CM-2(4)
Baseline Configuration | Unauthorized
Software
Withdrawn
CM-2(5)
Baseline Configuration | Authorized Software
Withdrawn
CM-2(6)
Baseline Configuration | Development and
Test Environments
CM-2(7)
Baseline Configuration | Configure Systems,
Components, or Devices for High-Risk Areas
X
X
CM-3
Configuration Change Control
+
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-10
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
CM-3(1)
Configuration Change Control | Automated
Document / Notification / Prohibition of
Changes
X
CM-3(2)
Configuration Change Control | Test /
Validate / Document Changes
X
X
CM-3(3)
Configuration Change Control | Automated
Change Implementation
CM-3(4)
Configuration Change Control | Security
Representative
+
+
+
CM-3(5)
Configuration Change Control | Automated
Security Response
+
CM-3(6)
Configuration Change Control | Cryptography
Management
+
+
+
CM-4
Security Impact Analysis
X
X
X
CM-4(1)
Security Impact Analysis | Separate Test
Environments
+
X
CM-4(2)
Security Impact Analysis | Verification of
Security Functions
CM-5
Access Restrictions For Change
+
X
X
CM-5(1)
Access Restrictions For Change | Automated
Access Enforcement / Auditing
+
X
CM-5(2)
Access Restrictions For Change | Review
System Changes
+
X
CM-5(3)
Access Restrictions For Change | Signed
Components
X
CM-5(4)
Access Restrictions For Change | Dual
Authorization
CM-5(5)
Access Restrictions For Change | Limit
Production / Operational Privileges
+
+
+
CM-5(6)
Access Restrictions For Change | Limit
Library Privileges
+
+
+
CM-5(7)
Access Restrictions For Change | Automatic
Implementation of Security Safeguards
Withdrawn
CM-6
Configuration Settings
X
X
X
CM-6(1)
Configuration Settings | Automated Central
Management / Application / Verification
+
X
CM-6(2)
Configuration Settings | Respond to
Unauthorized Changes
X
CM-6(3)
Configuration Settings | Unauthorized
Change Detection
Withdrawn
CM-6(4)
Configuration Settings | Conformance
Demonstration
Withdrawn
CM-7
Least Functionality
X
X
X
X
X
X
CM-7(1)
Least Functionality | Periodic Review
+
X
X
+
X
X
CM-7(2)
Least Functionality | Prevent Program
Execution
+
X
X
+
X
X
CM-7(3)
Least Functionality | Registration Compliance
+
+
+
+
+
+
CM-7(4)
Least Functionality | Unauthorized Software /

CNSSI No. 1253
D-11
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Blacklisting
CM-7(5)
Least Functionality | Authorized Software /
Whitelisting
+
+
X
+
+
X
CM-8
Information System Component Inventory
X
X
X
CM-8(1)
Information System Component Inventory |
Updates During Installations / Removals
X
X
CM-8(2)
Information System Component Inventory |
Automated Maintenance
+
+
X
CM-8(3)
Information System Component Inventory |
Automated Unauthorized Component
Detection
+
X
X
CM-8(4)
Information System Component Inventory |
Accountability Information
X
X
CM-8(5)
Information System Component Inventory |
No Duplicate Accounting of Components
X
X
CM-8(6)
Information System Component Inventory |
Assessed Configurations / Approved
Deviations
CM-8(7)
Information System Component Inventory |
Centralized Repository
CM-8(8)
Information System Component Inventory |
Automated Location Tracking
CM-8(9)
Information System Component Inventory |
Assignment of Components to Systems
CM-9
Configuration Management Plan
+
X
X
CM-9(1)
Configuration Management Plan |
Assignment of Responsibility
CM-10
Software Usage Restrictions
X
X
X
CM-10(1)
Software Usage Restrictions | Open Source
Software
+
+
+
CM-11
User-Installed Software
X
X
X
X
X
X
CM-11(1)
User-Installed Software | Alerts For
Unauthorized Installations
+
+
CM-11(2)
User-Installed Software | Prohibit Installation
without Privileged Status
+
+
+
+
+
+
CP-1
Contingency Planning Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CP-2
Contingency Plan
X
X
X
CP-2(1)
Contingency Plan | Coordinate With Related
Plans
X
X
CP-2(2)
Contingency Plan | Capacity Planning
X
CP-2(3)
Contingency Plan | Resume Essential
Missions / Business Functions
X
X
CP-2(4)
Contingency Plan | Resume All Missions /
Business Functions
X
CP-2(5)
Contingency Plan | Continue Essential
Missions / Business Functions
X
CP-2(6)
Contingency Plan | Alternate Processing /

CNSSI No. 1253
D-12
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Storage Site
CP-2(7)
Contingency Plan | Coordinate With External
Service Providers
CP-2(8)
Contingency Plan | Identify Critical Assets
X
X
CP-3
Contingency Training
X
X
X
CP-3(1)
Contingency Training | Simulated Events
X
CP-3(2)
Contingency Training | Automated Training
Environments
CP-4
Contingency Plan Testing
X
X
X
CP-4(1)
Contingency Plan Testing | Coordinate With
Related Plans
X
X
CP-4(2)
Contingency Plan Testing | Alternate
Processing Site
X
CP-4(3)
Contingency Plan Testing | Automated
Testing
CP-4(4)
Contingency Plan Testing | Full Recovery /
Reconstitution
CP-5
Contingency Plan Update
Withdrawn
CP-6
Alternate Storage Site
X
X
CP-6(1)
Alternate Storage Site | Separation From
Primary Site
X
X
CP-6(2)
Alternate Storage Site | Recovery Time /
Point Objectives
X
CP-6(3)
Alternate Storage Site | Accessibility
X
X
CP-7
Alternate Processing Site
X
X
X
X
X
X
CP-7(1)
Alternate Processing Site | Separation From
Primary Site
X
X
CP-7(2)
Alternate Processing Site | Accessibility
X
X
CP-7(3)
Alternate Processing Site | Priority of Service
X
X
CP-7(4)
Alternate Processing Site | Preparation for
Use
X
CP-7(5)
Alternate Processing Site | Equivalent
Information Security Safeguards
Withdrawn
CP-7(6)
Alternate Processing Site | Inability to Return
to Primary Site
CP-8
Telecommunications Services
X
X
CP-8(1)
Telecommunications Services | Priority of
Service Provisions
X
X
CP-8(2)
Telecommunications Services | Single Points
of Failure
X
X
CP-8(3)
Telecommunications Services | Separation of
Primary / Alternate Providers
X
CP-8(4)
Telecommunications Services | Provider
Contingency Plan
X
CP-8(5)
Telecommunications Services | Alternate
Telecommunication Service Testing
+
CP-9
Information System Backup
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-13
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
CP-9(1)
Information System Backup | Testing For
Reliability / Integrity
X
X
X
X
CP-9(2)
Information System Backup | Test
Restoration Using Sampling
X
CP-9(3)
Information System Backup | Separate
Storage for Critical Information
X
CP-9(4)
Information System Backup | Protection
From Unauthorized Modification
Withdrawn
CP-9(5)
Information System Backup | Transfer to
Alternate Storage Site
+
X
CP-9(6)
Information System Backup | Redundant
Secondary System
CP-9(7)
Information System Backup | Dual
Authorization
CP-10
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution
X
X
X
CP-10(1)
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution | Contingency Plan Testing
Withdrawn
CP-10(2)
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution | Transaction Recovery
X
X
X
X
CP-10(3)
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution | Compensating Security
Controls
Withdrawn
CP-10(4)
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution | Restore Within Time Period
X
X
CP-10(5)
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution | Failover Capability
Withdrawn
CP-10(6)
Information System Recovery and
Reconstitution | Component Protection
CP-11
Alternate Communications Protocols
CP-12
Safe Mode
CP-13
Alternative Security Mechanisms
IA-1
Identification and Authentication Policy and
Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-2
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users)
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-2(1)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Network Access to
Privileged Accounts
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-2(2)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Network Access to
Non-Privileged Accounts
+
X
X
+
X
X
IA-2(3)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Local Access to
Privileged Accounts
X
X
X
X
IA-2(4)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Local Access to
Non-Privileged Accounts
+
X
+
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-14
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
IA-2(5)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Group
Authentication
+
+
+
+
+
+
IA-2(6)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Network Access to
Privileged Accounts - Separate Device
IA-2(7)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Network Access to
Non-Privileged Accounts - Separate Device
IA-2(8)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Network Access to
Privileged Accounts - Replay Resistant
+
X
X
+
X
X
IA-2(9)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Network Access to
Non-Privileged Accounts - Replay Resistant
+
X
+
X
IA-2(10)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Single Sign-On
IA-2(11)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Remote Access -
Separate Device
+
X
X
+
X
X
IA-2(12)
Identification and Authentication
(Organizational Users) | Acceptance of PIV
Credentials
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-2(13)
Identification and Authentication | Out-of-
Band Authentication
IA-3
Device Identification and Authentication
+
X
X
+
X
X
IA-3(1)
Device Identification and Authentication |
Cryptographic Bidirectional Authentication
+
+
+
+
IA-3(2)
Device Identification and Authentication |
Cryptographic Bidirectional Network
Authentication
Withdrawn
IA-3(3)
Device Identification and Authentication |
Dynamic Address Allocation
IA-3(4)
Device Identification and Authentication |
Device Attestation
IA-4
Identifier Management
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-4(1)
Identifier Management | Prohibit Account
Identifiers As Public Identifiers
IA-4(2)
Identifier Management | Supervisor
Authorization
IA-4(3)
Identifier Management | Multiple Forms of
Certification
IA-4(4)
Identifier Management | Identify User Status
+
+
+
+
+
+
IA-4(5)
Identifier Management | Dynamic
Management
IA-4(6)
Identifier Management | Cross-Organization
Management
IA-4(7)
Identifier Management | In Person
Registration
IA-5
Authenticator Management
X
X
X
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-15
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
IA-5(1)
Authenticator Management | Password-Based
Authentication
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-5(2)
Authenticator Management | PKI-Based
Authentication
X
X
X
X
IA-5(3)
Authenticator Management | In Person or
Trusted Third-Party Registration
X
X
IA-5(4)
Authenticator Management | Automated
Support for Password Strength Determination
+
+
+
+
+
+
IA-5(5)
Authenticator Management | Change
Authenticators Prior to Delivery
IA-5(6)
Authenticator Management | Protection of
Authenticators
IA-5(7)
Authenticator Management | No Embedded
Unencrypted Static Authenticators
+
+
+
IA-5(8)
Authenticator Management | Multiple
Information System Accounts
+
+
+
+
+
+
IA-5(9)
Authenticator Management | Cross-
Organization Credential Management
IA-5(10)
Authenticator Management | Dynamic
Credential Association
IA-5(11)
Authenticator Management | Hardware
Token-Based Authentication
X
X
X
IA-5(12)
Authenticator Management | Biometric
Authentication
IA-5(13)
Authenticator Management | Expiration of
Cached Authenticators
+
+
+
+
+
+
IA-5(14)
Authenticator Management | Managing
Content of PKI Trust stores
+
+
+
+
+
+
IA-5(15)
Authenticator Management | FICAM-
Approved Products and Services
IA-6
Authenticator Feedback
X
X
X
IA-7
Cryptographic Module Authentication
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-8
Identification and Authentication (Non-
Organizational Users)
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-8(1)
Identification and Authentication (Non-
Organizational Users) | Acceptance of PIV
Credentials from Other Agencies
X
X
X
X
X
X
IA-8(2)
Identification and Authentication (Non-
Organizational Users) | Acceptance of Third-
Party Credentials
X
X
X
IA-8(3)
Identification and Authentication (Non-
Organizational Users) | Use of FICAM-
Approved Products
X
X
X
IA-8(4)
Identification and Authentication (Non-
Organizational Users) | Use of FICAM-Issued
Profiles
X
X
X
IA-8(5)
Identification and Authentication (Non-
Organizational Users) | Acceptance of PIV-I
Credentials

CNSSI No. 1253
D-16
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
IA-9
Service Identification and Authentication
IA-9(1)
Service Identification and Authentication |
Information Exchange
IA-9(2)
Service Identification and Authentication |
Transmission of Decisions
IA-10
Adaptive Identification and Authentication
+
+
IA-11
Re-authentication
+
+
IR-1
Incident Response Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-2
Incident Response Training
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-2(1)
Incident Response Training | Simulated
Events
X
X
X
IR-2(2)
Incident Response Training | Automated
Training Environments
X
X
IR-3
Incident Response Testing
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
IR-3(1)
Incident Response Testing | Automated
Testing
IR-3(2)
Incident Response Testing | Coordination
With Related Plans
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-4
Incident Handling
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-4(1)
Incident Handling | Automated Incident
Handling Processes
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-4(2)
Incident Handling | Dynamic Reconfiguration
IR-4(3)
Incident Handling | Continuity of Operations
+
+
+
+
+
+
IR-4(4)
Incident Handling | Information Correlation
+
+
X
+
+
X
+
+
X
IR-4(5)
Incident Handling | Automatic Disabling of
Information System
IR-4(6)
Incident Handling | Insider Threats - Specific
Capabilities
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
IR-4(7)
Incident Handling | Insider Threats - Intra-
Organization Coordination
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
IR-4(8)
Incident Handling | Correlation With External
Organizations
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
IR-4(9)
Incident Handling | Dynamic Response
Capability
IR-4(10)
Incident Handling | Supply Chain
Coordination
IR-5
Incident Monitoring
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-5(1)
Incident Monitoring | Automated Tracking /
Data Collection / Analysis
X
X
X
IR-6
Incident Reporting
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-6(1)
Incident Reporting | Automated Reporting
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-6(2)
Incident Reporting | Vulnerabilities Related
to Incidents
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
IR-6(3)
Incident Reporting | Coordination With
Supply Chain
IR-7
Incident Response Assistance
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CNSSI No. 1253
D-17
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
IR-7(1)
Incident Response Assistance | Automation
Support For Availability of Information /
Support
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-7(2)
Incident Response Assistance | Coordination
With External Providers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
IR-8
Incident Response Plan
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IR-9
Information Spillage Response
+
+
+
IR-9(1)
Information Spillage Response | Responsible
Personnel
+
+
+
IR-9(2)
Information Spillage Response | Training
+
+
+
IR-9(3)
Information Spillage Response | Post-Spill
Operations
+
+
IR-9(4)
Information Spillage Response | Exposure to
Unauthorized Personnel
+
+
+
IR-10
Integrated Information Security Cell
+
+
+
+
+
+
MA-1
System Maintenance Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
MA-2
Controlled Maintenance
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
MA-2(1)
Controlled Maintenance | Record Content
Withdrawn
MA-2(2)
Controlled Maintenance | Automated
Maintenance Activities
X
X
X
MA-3
Maintenance Tools
+
X
X
MA-3(1)
Maintenance Tools | Inspect Tools
X
X
MA-3(2)
Maintenance Tools | Inspect Media
+
X
X
MA-3(3)
Maintenance Tools | Prevent Unauthorized
Removal
+
+
X
MA-3(4)
Maintenance Tools | Restricted Tool Use
MA-4
Nonlocal Maintenance
X
X
X
MA-4(1)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Auditing and Review
+
+
MA-4(2)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Document Nonlocal
Maintenance
X
X
MA-4(3)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Comparable Security
/ Sanitization
+
+
X
+
+
X
MA-4(4)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Authentication /
Separation of Maintenance Sessions
MA-4(5)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Approvals and
Notifications
MA-4(6)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Cryptographic
Protection
+
+
+
+
+
+
MA-4(7)
Nonlocal Maintenance | Remote Disconnect
Verification
+
+
+
MA-5
Maintenance Personnel
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
MA-5(1)
Maintenance Personnel | Individuals Without
Appropriate Access
X
X
X
MA-5(2)
Maintenance Personnel | Security Clearances
For Classified Systems

CNSSI No. 1253
D-18
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
MA-5(3)
Maintenance Personnel | Citizenship
Requirements For Classified Systems
MA-5(4)
Maintenance Personnel | Foreign Nationals
MA-5(5)
Maintenance Personnel | Non System-Related
Maintenance
MA-6
Timely Maintenance
X
X
MA-6(1)
Timely Maintenance | Preventive
Maintenance
MA-6(2)
Timely Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance
MA-6(3)
Timely Maintenance | Automated Support for
Predictive Maintenance
MP-1
Media Protection Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
MP-2
Media Access
X
X
X
X
X
X
MP-2(1)
Media Access | Automated Restricted Access
Withdrawn
MP-2(2)
Media Access | Cryptographic Protection
Withdrawn
MP-3
Media Marking
X
X
MP-4
Media Storage
X
X
X
X
MP-4(1)
Media Storage | Cryptographic Protection
Withdrawn
MP-4(2)
Media Storage | Automated Restricted Access
MP-5
Media Transport
X
X
X
X
MP-5(1)
Media Transport | Protection Outside of
Controlled Areas
Withdrawn
MP-5(2)
Media Transport | Documentation of
Activities
Withdrawn
MP-5(3)
Media Transport | Custodians
MP-5(4)
Media Transport | Cryptographic Protection
X
X
X
X
MP-6
Media Sanitization
X
X
X
MP-6(1)
Media Sanitization | Review / Approve /
Track / Document / Verify
X
MP-6(2)
Media Sanitization | Equipment Testing
X
MP-6(3)
Media Sanitization | Nondestructive
Techniques
X
MP-6(4)
Media Sanitization | Controlled Unclassified
Information
Withdrawn
MP-6(5)
Media Sanitization | Classified Information
Withdrawn
MP-6(6)
Media Sanitization | Media Destruction
Withdrawn
MP-6(7)
Media Sanitization | Dual Authorization
MP-6(8)
Media Sanitization | Remote Purging /
Wiping of Information
MP-7
Media Use
X
X
X
X
X
X
MP-7(1)
Media Use | Prohibit Use without Owner
+
X
X
MP-7(2)
Media Use | Prohibit Use of Sanitization-
Resistant Media
MP-8
Media Downgrading

CNSSI No. 1253
D-19
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
MP-8(1)
Media Downgrading | Documentation of
Process
MP-8(2)
Media Downgrading | Equipment Testing
MP-8(3)
Media Downgrading | Controlled
Unclassified Information
MP-8(4)
Media Downgrading | Classified Information
PE-1
Physical and Environmental Protection Policy
and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-2
Physical Access Authorizations
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-2(1)
Physical Access Authorizations | Access by
Position / Role
PE-2(2)
Physical Access Authorizations | Two Forms
of Identification
PE-2(3)
Physical Access Authorizations | Restrict
Unescorted Access
PE-3
Physical Access Control
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-3(1)
Physical Access Control | Information System
Access
+
+
X
+
+
X
PE-3(2)
Physical Access Control | Facility /
Information System Boundaries
PE-3(3)
Physical Access Control | Continuous Guards
/ Alarms / Monitoring
PE-3(4)
Physical Access Control | Lockable Casings
PE-3(5)
Physical Access Control | Tamper Protection
PE-3(6)
Physical Access Control | Facility Penetration
Testing
PE-4
Access Control For Transmission Medium
X
X
X
X
PE-5
Access Control For Output Devices
X
X
PE-5(1)
Access Control For Output Devices | Access
to Output by Authorized Individuals
PE-5(2)
Access Control For Output Devices | Access
to Output by Individual Identity
PE-5(3)
Access Control For Output Devices | Marking
Output Devices
PE-6
Monitoring Physical Access
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-6(1)
Monitoring Physical Access | Intrusion
Alarms / Surveillance Equipment
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-6(2)
Monitoring Physical Access | Automated
Intrusion Recognition / Responses
PE-6(3)
Monitoring Physical Access | Video
Surveillance
PE-6(4)
Monitoring Physical Access | Monitoring
Physical Access to Information Systems
X
X
X
PE-7
Visitor Control
Withdrawn
PE-7(1)
Visitor Control
Withdrawn
PE-7(2)
Visitor Control
Withdrawn

CNSSI No. 1253
D-20
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
PE-8
Visitor Access Records
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-8(1)
Visitor Access Records | Automated Records
Maintenance / Review
X
X
PE-8(2)
Visitor Access Records | Physical Access
Records
Withdrawn
PE-9
Power Equipment and Cabling
X
X
PE-9(1)
Power Equipment and Cabling | Redundant
Cabling
PE-9(2)
Power Equipment and Cabling | Automatic
Voltage Controls
PE-10
Emergency Shutoff
X
X
PE-10(1)
Emergency Shutoff | Accidental /
Unauthorized Activation
Withdrawn
PE-11
Emergency Power
X
X
PE-11(1)
Emergency Power | Long-Term Alternate
Power Supply - Minimal Operational
Capability
X
PE-11(2)
Emergency Power | Long-Term Alternate
Power Supply - Self-Contained
PE-12
Emergency Lighting
X
X
X
PE-12(1)
Emergency Lighting | Essential Missions /
Business Functions
PE-13
Fire Protection
X
X
X
PE-13(1)
Fire Protection | Detection Devices / Systems
X
PE-13(2)
Fire Protection | Suppression Devices /
Systems
X
PE-13(3)
Fire Protection | Automatic Fire Suppression
X
X
PE-13(4)
Fire Protection | Inspections
+
PE-14
Temperature and Humidity Controls
X
X
X
PE-14(1)
Temperature and Humidity Controls |
Automatic Controls
PE-14(2)
Temperature and Humidity Controls |
Monitoring With Alarms / Notifications
PE-15
Water Damage Protection
X
X
X
PE-15(1)
Water Damage Protection | Automation
Support
X
PE-16
Delivery and Removal
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-17
Alternate Work Site
X
X
X
X
X
X
PE-18
Location of Information System Components
X
PE-18(1)
Location of Information System Components
| Facility Site
PE-19
Information Leakage
PE-19(1)
Information Leakage | National Emissions /
TEMPEST Policies and Procedures
PE-20
Asset Monitoring and Tracking

CNSSI No. 1253
D-21
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
PL-1
Security Planning Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PL-2
System Security Plan
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PL-2(1)
System Security Plan | Concept of Operations
Withdrawn
PL-2(2)
System Security Plan | Functional
Architecture
Withdrawn
PL-2(3)
System Security Plan | Plan / Coordinate
With Other Organizational Entities
X
X
X
X
X
X
PL-3
System Security Plan Update
Withdrawn
PL-4
Rules of Behavior
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PL-4(1)
Rules of Behavior | Social Media and
Networking Restrictions
X
X
PL-5
Privacy Impact Assessment
Withdrawn
PL-6
Security-Related Activity Planning
Withdrawn
PL-7
Security Concept of Operations
PL-8
Information Security Architecture
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
PL-8(1)
Information Security Architecture | Defense-
in-Depth
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
PL-8(2)
Information Security Architecture | Supplier
Diversity
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
PL-9
Central Management
PS-1
Personnel Security Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-2
Position Risk Designation
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-3
Personnel Screening
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-3(1)
Personnel Screening | Classified Information
PS-3(2)
Personnel Screening | Formal Indoctrination
PS-3(3)
Personnel Screening | Information With
Special Protection Measures
PS-4
Personnel Termination
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-4(1)
Personnel Termination | Post-Employment
Requirements
+
+
+
PS-4(2)
Personnel Termination | Automated
Notification
X
X
X
PS-5
Personnel Transfer
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-6
Access Agreements
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-6(1)
Access Agreements | Information Requiring
Special Protection
Withdrawn
PS-6(2)
Access Agreements | Classified Information
Requiring Special Protection
PS-6(3)
Access Agreements | Post-Employment
Requirements
+
+
+
PS-7
Third-Party Personnel Security
X
X
X
X
X
X
PS-8
Personnel Sanctions
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
RA-1
Risk Assessment Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
RA-2
Security Categorization
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-22
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
RA-3
Risk Assessment
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
RA-4
Risk Assessment Update
Withdrawn
RA-5
Vulnerability Scanning
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
RA-5(1)
Vulnerability Scanning | Update Tool
Capability
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
RA-5(2)
Vulnerability Scanning | Update by
Frequency / Prior to New Scan / When
Identified
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
RA-5(3)
Vulnerability Scanning | Breadth /Depth of
Coverage
RA-5(4)
Vulnerability Scanning | Discoverable
Information
+
+
X
+
+
X
+
+
X
RA-5(5)
Vulnerability Scanning | Privileged Access
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
RA-5(6)
Vulnerability Scanning | Automated Trend
Analyses
RA-5(7)
Vulnerability Scanning | Automated
Detection and Notification of Unauthorized
Components
Withdrawn
RA-5(8)
Vulnerability Scanning | Review Historic
Audit Logs
RA-5(9)
Vulnerability Scanning | Penetration Testing
and Analyses
Withdrawn
RA-5(10)
Vulnerability Scanning | Correlate Scanning
Information
+
+
+
RA-6
Technical Surveillance Countermeasures
Survey
SA-1
System and Services Acquisition Policy and
Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-2
Allocation of Resources
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-3
System Development Life Cycle
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-4
Acquisition Process
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-4(1)
Acquisition Process | Functional Properties of
Security Controls
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-4(2)
Acquisition Process | Design /
Implementation Information for Security
Controls
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-4(3)
Acquisition Process | Development Methods /
Techniques / Practices
+
SA-4(4)
Acquisition Process | Assignment of
Components to Systems
Withdrawn
SA-4(5)
Acquisition Process | System / Component /
Service Configurations
+
SA-4(6)
Acquisition Process | Use of Information
Assurance Products
SA-4(7)
Acquisition Process | NIAP-Approved
Protection Profiles
+
+
+
SA-4(8)
Acquisition Process | Continuous Monitoring
Plan

CNSSI No. 1253
D-23
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SA-4(9)
Acquisition Process | Functions / Ports /
Protocols / Services in Use
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
SA-4(10)
Acquisition Process | Use of Approved PIV
Products
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-5
Information System Documentation
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-5(1)
Information System Documentation |
Functional Properties of Security Controls
Withdrawn
SA-5(2)
Information System Documentation |
Security-Relevant External System Interfaces
Withdrawn
SA-5(3)
Information System Documentation | High-
Level Design
Withdrawn
SA-5(4)
Information System Documentation | Low-
Level Design
Withdrawn
SA-5(5)
Information System Documentation | Source
Code
Withdrawn
SA-6
Software Usage Restrictions
Withdrawn
SA-6(1)
Software Usage Restrictions
Withdrawn
SA-7
User-Installed Software
Withdrawn
SA-8
Security Engineering Principles
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
SA-9
External Information System Services
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SA-9(1)
External Information Systems | Risk
Assessments / Organizational Approvals
+
+
+
SA-9(2)
External Information Systems | Identification
of Functions / Ports / Protocols / Services
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
SA-9(3)
External Information Systems | Establish /
Maintain Trust Relationship with Providers
SA-9(4)
External Information Systems | Consistent
Interests of Consumers and Providers
SA-9(5)
External Information Systems | Processing,
Storage, and Service Location
SA-10
Developer Configuration Management
+
X
X
SA-10(1)
Developer Configuration Management |
Software / Firmware Integrity Verification
+
+
+
SA-10(2)
Developer Configuration Management |
Alternative Configuration Management
Processes
SA-10(3)
Developer Configuration Management |
Hardware Integrity Verification
SA-10(4)
Developer Configuration Management |
Trusted Generation
SA-10(5)
Developer Configuration Management |
Mapping Integrity for Version Control
SA-10(6)
Developer Configuration Management |
Trusted Distribution
SA-11
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation
X
X
X
X
X
X
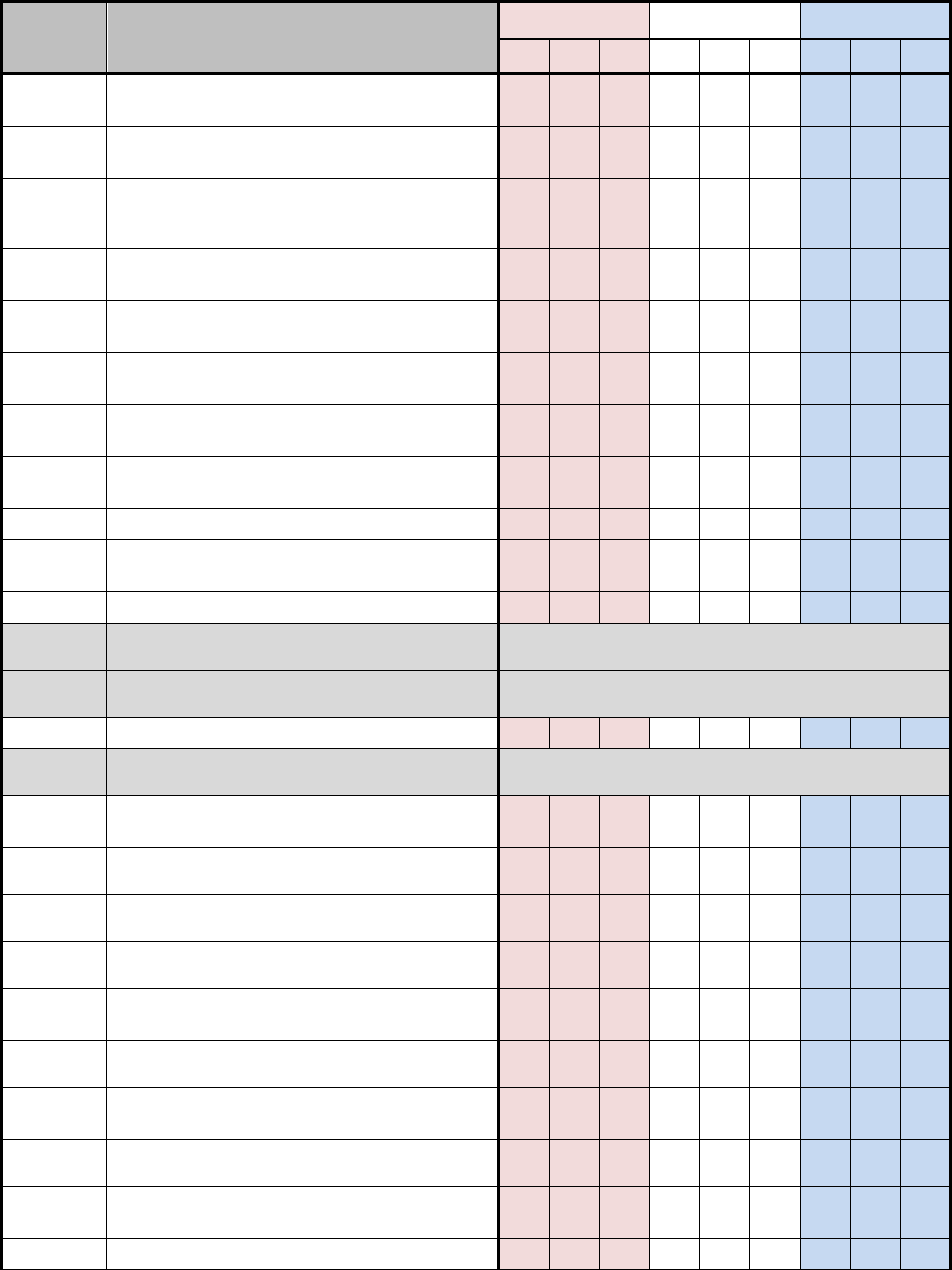
CNSSI No. 1253
D-24
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SA-11(1)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Static Code Analysis
SA-11(2)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Threat and Vulnerability Analyses
SA-11(3)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Independent Verification of Assessment
Plans / Evidence
SA-11(4)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Manual Code Reviews
SA-11(5)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Penetration Testing / Analysis
SA-11(6)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Attack Surface Reviews
SA-11(7)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Verify Scope of Testing / Evaluation
SA-11(8)
Developer Security Testing and Evaluation |
Dynamic Code Analysis
SA-12
Supply Chain Protection
+
+
X
+
+
X
+
+
X
SA-12(1)
Supply Chain Protection | Acquisition
Strategies / Tools / Methods
+
+
+
SA-12(2)
Supply Chain Protection | Supplier Reviews
SA-12(3)
Supply Chain Protection | Trusted Shipping
and Warehousing
Withdrawn
SA-12(4)
Supply Chain Protection | Diversity of
Suppliers
Withdrawn
SA-12(5)
Supply Chain Protection | Limitation of Harm
+
+
+
SA-12(6)
Supply Chain Protection | Minimizing
Procurement Time
Withdrawn
SA-12(7)
Supply Chain Protection | Assessments Prior
to Selection / Acceptance / Update
SA-12(8)
Supply Chain Protection | Use of All-Source
Intelligence
+
+
+
SA-12(9)
Supply Chain Protection | Operations
Security
+
+
+
SA-
12(10)
Supply Chain Protection | Validate As
Genuine and Not Altered
SA-
12(11)
Supply Chain Protection | Penetration Testing
/ Analysis of Elements, Processes, and Actors
+
+
+
SA-
12(12)
Supply Chain Protection | Inter-
Organizational Agreements
SA-
12(13)
Supply Chain Protection | Critical
Information System Components
SA-
12(14)
Supply Chain Protection | Identity and
Traceability
SA-
12(15)
Supply Chain Protection | Processes to
Address Weaknesses or Deficiencies
SA-13
Trustworthiness

CNSSI No. 1253
D-25
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SA-14
Criticality Analysis
+
+
+
SA-14(1)
Criticality Analysis / Critical Components
with No Viable Alternative Sourcing
Withdrawn
SA-15
Development Process, Standards, and Tools
+
+
X
+
+
X
+
+
X
SA-15(1)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Quality Metrics
SA-15(2)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Security Tracking Tools
SA-15(3)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Criticality Analysis
+
+
+
SA-15(4)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Threat Modeling / Vulnerability Analysis
+
+
+
SA-15(5)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Attack Surface Reduction
SA-15(6)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Continuous Improvement
SA-15(7)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Automated Vulnerability Analysis
+
SA-15(8)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Reuse of Threat / Vulnerability Information
SA-15(9)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Use of Live Data
+
+
+
SA-
15(10)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Incident Response Plan
SA-
15(11)
Development Process, Standards, and Tools |
Archive Information System / Component
SA-16
Developer-Provided Training
X
X
X
SA-17
Developer Security Architecture and Design
X
X
X
SA-17(1)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Formal Policy Model
SA-17(2)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Security-Relevant Components
SA-17(3)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Formal Correspondence
SA-17(4)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Informal Correspondence
SA-17(5)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Conceptually Simple Design
SA-17(6)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Structure for Testing
SA-17(7)
Developer Security Architecture and Design |
Structure for Least Privilege
SA-18
Tamper Resistance and Detection
SA-18(1)
Tamper Resistance and Detection | Multiple
Phases of SDLC

CNSSI No. 1253
D-26
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SA-18(2)
Tamper Resistance and Detection | Inspection
of Information Systems, Components, or
Devices
SA-19
Component Authenticity
+
+
+
SA-19(1)
Component Authenticity | Anti-Counterfeit
Training
SA-19(2)
Component Authenticity | Configuration
Control for Component Service / Repair
SA-19(3)
Component Authenticity | Component
Disposal
SA-19(4)
Component Authenticity | Anti-Counterfeit
Scanning
SA-20
Customized Development of Critical
Components
SA-21
Developer Screening
SA-21(1)
Developer Screening | Validation of
Screening
SA-22
Unsupported System Components
+
+
+
SA-22(1)
Unsupported System Components |
Alternative Sources for Continued Support
SC-1
System and Communications Protection
Policy and Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SC-2
Application Partitioning
X
X
X
X
SC-2(1)
Application Partitioning | Interfaces For Non-
Privileged Users
SC-3
Security Function Isolation
X
X
SC-3(1)
Security Function Isolation | Hardware
Separation
SC-3(2)
Security Function Isolation | Access / Flow
Control Functions
SC-3(3)
Security Function Isolation | Minimize
Nonsecurity Functionality
SC-3(4)
Security Function Isolation | Module
Coupling and Cohesiveness
SC-3(5)
Security Function Isolation | Layered
Structures
SC-4
Information In Shared Resources
X
X
SC-4(1)
Information In Shared Resources | Security
Levels
Withdrawn
SC-4(2)
Information In Shared Resources | Periods
Processing
SC-5
Denial of Service Protection
X
X
X
SC-5(1)
Denial of Service Protection | Restrict
Internal Users
+
+
+
SC-5(2)
Denial of Service Protection | Excess
Capacity / Bandwidth / Redundancy
+
+
SC-5(3)
Denial of Service Protection | Detection /
Monitoring
+
+

CNSSI No. 1253
D-27
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SC-6
Resource Availability
SC-7
Boundary Protection
X
X
X
X
X
X
SC-7(1)
Boundary Protection | Physically Separated
Subnetworks
Withdrawn
SC-7(2)
Boundary Protection | Public Access
Withdrawn
SC-7(3)
Boundary Protection | Access Points
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-7(4)
Boundary Protection | External
Telecommunications Services
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-7(5)
Boundary Protection | Deny by Default /
Allow by Exception
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-7(6)
Boundary Protection | Response to
Recognized Failures
Withdrawn
SC-7(7)
Boundary Protection | Prevent Split
Tunneling for Remote Devices
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-7(8)
Boundary Protection | Route Traffic to
Authenticated Proxy Servers
+
+
X
+
+
X
SC-7(9)
Boundary Protection | Restrict Threatening
Outgoing Communications Traffic
+
+
+
SC-7(10)
Boundary Protection | Prevent Unauthorized
Exfiltration
+
+
+
SC-7(11)
Boundary Protection | Restrict Incoming
Communications Traffic
+
+
+
SC-7(12)
Boundary Protection | Host-Based Protection
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SC-7(13)
Boundary Protection | Isolation of Security
Tools / Mechanisms / Support Components
+
+
+
+
+
+
SC-7(14)
Boundary Protection | Protect Against
Unauthorized Physical Connections
+
+
+
+
+
+
SC-7(15)
Boundary Protection | Route Privileged
Network Accesses
SC-7(16)
Boundary Protection | Prevent Discovery of
Components / Devices
SC-7(17)
Boundary Protection | Automated
Enforcement of Protocol Formats
SC-7(18)
Boundary Protection | Fail Secure
X
X
X
SC-7(19)
Boundary Protection | Block Communication
from Non-Organizationally Configured Hosts
SC-7(20)
Boundary Protection | Dynamic Isolation /
Segregation
SC-7(21)
Boundary Protection | Isolation of
Information System Components
X
X
SC-7(22)
Boundary Protection | Separate Subnets for
Connecting to Different Security Domains
SC-7(23)
Boundary Protection | Disable Sender
Feedback on Protocol Validation Failure
SC-8
Transmission Confidentiality and Integrity
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-8(1)
Transmission Confidentiality and Integrity |
Cryptographic or Alternate Physical
+
X
X
+
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-28
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Protection
SC-8(2)
Transmission Confidentiality and Integrity |
Pre / Post Transmission Handling
+
+
+
+
SC-8(3)
Transmission Confidentiality and Integrity |
Cryptographic Protection for Message
Externals
SC-8(4)
Transmission Confidentiality and Integrity |
Conceal / Randomize Communications
SC-9
Transmission Confidentiality
Withdrawn
SC-9(1)
Transmission Confidentiality | Cryptographic
or Alternate Physical Protection
Withdrawn
SC-9(2)
Transmission Confidentiality | Pre / Post
Transmission Handling
Withdrawn
SC-10
Network Disconnect
X
X
X
X
SC-11
Trusted Path
SC-11(1)
Trusted Path | Logical Isolation
SC-12
Cryptographic Key Establishment and
Management
X
X
X
X
X
X
SC-12(1)
Cryptographic Key Establishment and
Management | Availability
X
SC-12(2)
Cryptographic Key Establishment and
Management | Symmetric Keys
SC-12(3)
Cryptographic Key Establishment and
Management | Asymmetric Keys
SC-12(4)
Cryptographic Key Establishment and
Management | PKI Certificates
Withdrawn
SC-12(5)
Cryptographic Key Establishment and
Management | PKI Certificates / Hardware
Tokens
Withdrawn
SC-13
Cryptographic Protection
X
X
X
X
X
X
SC-13(1)
Cryptographic Protection | FIPS-Validated
Cryptography
Withdrawn
SC-13(2)
Cryptographic Protection | NSA-Approved
Cryptography
Withdrawn
SC-13(3)
Cryptographic Protection | Individuals
Without Formal Access Approvals
Withdrawn
SC-13(4)
Cryptographic Protection | Digital
Signatures
Withdrawn
SC-14
Public Access Protections
Withdrawn
SC-15
Collaborative Computing Devices
X
X
X
SC-15(1)
Collaborative Computing Devices | Physical
Disconnect
SC-15(2)
Collaborative Computing Devices | Blocking
Inbound / Outbound Communications Traffic
Withdrawn
SC-15(3)
Collaborative Computing Devices | Disabling
/ Removal In Secure Work Areas

CNSSI No. 1253
D-29
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SC-15(4)
Collaborative Computing Devices | Explicitly
Indicate Current Participants
SC-16
Transmission of Security Attributes
SC-16(1)
Transmission of Security Attributes | Integrity
Validation
SC-17
Public Key Infrastructure Certificates
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-18
Mobile Code
+
X
X
SC-18(1)
Mobile Code | Identify Unacceptable Code /
Take Corrective Actions
+
+
+
SC-18(2)
Mobile Code | Acquisition / Development /
Use
+
+
+
SC-18(3)
Mobile Code | Prevent Downloading /
Execution
+
+
+
SC-18(4)
Mobile Code | Prevent Automatic Execution
+
+
+
SC-18(5)
Mobile Code | Allow Execution Only In
Confined Environments
SC-19
Voice Over Internet Protocol
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-20
Secure Name / Address Resolution Service
(Authoritative Source)
X
X
X
SC-20(1)
Secure Name / Address Resolution Service
(Authoritative Source) | Child Subspaces
Withdrawn
SC-20(2)
Secure Name / Address Resolution Service
(Authoritative Source) | Data Origin /
Integrity
SC-21
Secure Name / Address Resolution Service
(Recursive or Caching Resolver)
X
X
X
SC-21(1)
Secure Name / Address Resolution Service
(Recursive or Caching Resolver) | Data
Origin / Integrity
Withdrawn
SC-22
Architecture and Provisioning for Name /
Address Resolution Service
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SC-23
Session Authenticity
+
X
X
SC-23(1)
Session Authenticity | Invalidate Session
Identifiers At Logout
+
+
+
SC-23(2)
Session Authenticity | User-Initiated Logouts
/ Message Displays
Withdrawn
SC-23(3)
Session Authenticity | Unique Session
Identifiers With Randomization
+
+
+
SC-23(4)
Session Authenticity | Unique Session
Identifiers With Randomization
Withdrawn
SC-23(5)
Session Authenticity | Allowed Certificate
Authorities
+
+
+
SC-24
Fail In Known State
X
X
SC-25
Thin Nodes
SC-26
Honeypots
SC-26(1)
Honeypots | Detection of Malicious Code
Withdrawn

CNSSI No. 1253
D-30
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SC-27
Platform-Independent Applications
SC-28
Protection of Information At Rest
+
X
X
+
X
X
SC-28(1)
Protection of Information At Rest |
Cryptographic Protection
+
+
+
+
+
+
SC-28(2)
Protection of Information At Rest | Off-Line
Storage
SC-29
Heterogeneity
SC-29(1)
Heterogeneity | Virtualization Techniques
SC-30
Concealment and Misdirection
SC-30(1)
Concealment and Misdirection |
Virtualization Techniques
Withdrawn
SC-30(2)
Concealment and Misdirection | Randomness
SC-30(3)
Concealment and Misdirection | Change
Processing / Storage Locations
SC-30(4)
Concealment and Misdirection | Misleading
Information
SC-30(5)
Concealment and Misdirection | Concealment
of System Components
SC-31
Covert Channel Analysis
SC-31(1)
Covert Channel Analysis | Test Covert
Channels for Exploitability
SC-31(2)
Covert Channel Analysis | Maximum
Bandwidth
SC-31(3)
Covert Channel Analysis | Measure
Bandwidth In Operational Environments
SC-32
Information System Partitioning
SC-33
Transmission Preparation Integrity
Withdrawn
SC-34
Non-modifiable executable programs
SC-34(1)
Non-Modifiable Executable Programs | No
Writable Storage
SC-34(2)
Non-Modifiable Executable Programs |
Integrity Protection / Read-Only Media
SC-34(3)
Non-Modifiable Executable Programs |
Hardware-Based Protection
SC-35
Honeyclients
SC-36
Distributed Processing and Storage
SC-36(1)
Distributed Processing and Storage | Polling
Techniques
SC-37
Out-of-Band Channels
SC-37(1)
Out-Of-Band Channels | Ensure Delivery /
Transmission
SC-38
Operations Security
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SC-39
Process Isolation
X
X
X
X
X
X
SC-39(1)
Process Isolation | Hardware Separation
SC-39(2)
Process Isolation | Thread Isolation

CNSSI No. 1253
D-31
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SC-40
Wireless Link Protection
SC-40(1)
Wireless Link Protection | Electromagnetic
Interference
SC-40(2)
Wireless Link Protection | Reduce Detection
Potential
SC-40(3)
Wireless Link Protection | Imitative or
Manipulative Communications Deception
SC-40(4)
Wireless Link Protection | Signal Parameter
Identification
SC-41
Port and I/O Device Access
SC-42
Sensor Capability and Data
SC-42(1)
Sensor Capability and Data | Reporting to
Authorized Individuals or Roles
SC-42(2)
Sensor Capability and Data | Authorized Use
SC-42(3)
Sensor Capability and Data | Prohibit Use of
Devices
SC-43
Usage Restrictions
SC-44
Detonation Chambers
SI-1
System and Information Integrity Policy and
Procedures
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SI-2
Flaw Remediation
X
X
X
SI-2(1)
Flaw Remediation | Central Management
+
+
X
SI-2(2)
Flaw Remediation | Automated Flaw
Remediation Status
+
X
X
SI-2(3)
Flaw Remediation | Time to Remediate Flaws
/ Benchmarks for Corrective Actions
+
+
+
SI-2(4)
Flaw Remediation | Automated Patch
Management Tools
Withdrawn
SI-2(5)
Flaw Remediation | Automatic software /
Firmware Updates
SI-2(6)
Flaw Remediation | Removal of Previous
Versions of Software / Firmware
+
+
+
SI-3
Malicious Code Protection
X
X
X
SI-3(1)
Malicious Code Protection | Central
Management
+
X
X
SI-3(2)
Malicious Code Protection | Automatic
Updates
+
X
X
SI-3(3)
Malicious Code Protection | Non-Privileged
Users
Withdrawn
SI-3(4)
Malicious Code Protection | Updates Only by
Privileged Users
SI-3(5)
Malicious Code Protection | Portable Storage
Devices
Withdrawn
SI-3(6)
Malicious Code Protection | Testing /
Verification
SI-3(7)
Malicious Code Protection | Non Signature-
Based Detection

CNSSI No. 1253
D-32
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SI-3(8)
Malicious Code Protection | Detect
Unauthorized Commands
SI-3(9)
Malicious Code Protection | Authenticate
Remote commands
SI-3(10)
Malicious Code Protection | Malicious Code
Analysis
+
+
+
SI-4
Information System Monitoring
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SI-4(1)
Information System Monitoring | System-
Wide Intrusion Detection System
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(2)
Information System Monitoring | Automated
Tools For Real-Time Analysis
X
X
X
X
X
X
SI-4(3)
Information System Monitoring | Automated
Tool Integration
SI-4(4)
Information System Monitoring | Inbound
and Outbound Communications Traffic
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
SI-4(5)
Information System Monitoring | System-
Generated Alerts
+
X
X
+
X
X
+
X
X
SI-4(6)
Information System Monitoring | Restrict
Non-Privileged Users
Withdrawn
SI-4(7)
Information System Monitoring | Automated
Response to Suspicious Events
SI-4(8)
Information System Monitoring | Protection
of Monitoring Information
Withdrawn
SI-4(9)
Information System Monitoring | Testing of
Monitoring Tools
SI-4(10)
Information System Monitoring | Visibility of
Encrypted Communications
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(11)
Information System Monitoring | Analyze
Communications Traffic Anomalies
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(12)
Information System Monitoring | Automated
Alerts
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(13)
Information System Monitoring | Analyze
Traffic / Event Patterns
SI-4(14)
Information System Monitoring | Wireless
Intrusion Detection
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(15)
Information System Monitoring | Wireless to
Wireline Communications
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(16)
Information System Monitoring | Correlate
Monitoring Information
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(17)
Information System Monitoring | Integrated
Situational Awareness
SI-4(18)
Information System Monitoring | Analyze
Traffic / Covert Exfiltration
SI-4(19)
Information System Monitoring | Individuals
Posing Greater Risk
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(20)
Information System Monitoring | Privileged
User
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(21)
Information System Monitoring |

CNSSI No. 1253
D-33
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
Probationary Periods
SI-4(22)
Information System Monitoring |
Unauthorized Network Services
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(23)
Information System Monitoring | Host-Based
Devices
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
SI-4(24)
Information System Monitoring | Indicators
of Compromise
SI-5
Security Alerts, Advisories, and Directives
X
X
X
SI-5(1)
Security Alerts, Advisories, and Directives |
Automated Alerts and Advisories
X
SI-6
Security Function Verification
X
SI-6(1)
Security Function Verification | Notification
of Failed Security Tests
Withdrawn
SI-6(2)
Security Function Verification | Automation
Support For Distributed Testing
SI-6(3)
Security Function Verification | Report
Verification Results
+
SI-7
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity
X
X
SI-7(1)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Integrity Checks
X
X
SI-7(2)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Automated Notifications of
Integrity Violations
X
SI-7(3)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Centrally-Managed Integrity Tools
SI-7(4)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Tamper-Evident Packaging
Withdrawn
SI-7(5)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Automated Response to Integrity
Violations
X
SI-7(6)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Cryptographic Protection
SI-7(7)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Integration of Detection and
Response
X
X
SI-7(8)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Auditing Capability For Significant
Events
+
+
SI-7(9)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Verify Boot Process
SI-7(10)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Protection of Boot Firmware
SI-7(11)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Confined Environments With
Limited Privileges
SI-7(12)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Integrity Verification

CNSSI No. 1253
D-34
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SI-7(13)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Code Execution In Protected
Environments
SI-7(14)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Binary or Machine Executable
Code
+
+
X
SI-7(15)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Code Authentication
SI-7(16)
Software, Firmware, and Information
Integrity | Time Limit on Process Execution
without Supervision
SI-8
Spam Protection
X
X
X
X
SI-8(1)
Spam Protection | Central Management of
Protection Mechanisms
X
X
X
X
SI-8(2)
Spam Protection | Automatic Updates
X
X
X
X
SI-8(3)
Spam Protection | Continuous Learning
Capability
SI-9
Information Input Restrictions
Withdrawn
SI-10
Information Input Validation
+
X
X
SI-10(1)
Information Input Validation | Manual
Override Capability
SI-10(2)
Information Input Validation | Review /
Resolution of Errors
SI-10(3)
Information Input Validation | Predictable
Behavior
+
+
SI-10(4)
Information Input Validation | Review /
Timing Interactions
SI-10(5)
Information Input Validation | Review /
Restrict Inputs to Trusted Sources and
Approved Formats
SI-11
Error Handling
+
X
X
SI-12
Information Handling and Retention
X
X
X
X
X
X
SI-13
Predictable Failure Prevention
SI-13(1)
Predictable Failure Prevention | Transferring
Component Responsibilities
SI-13(2)
Predictable Failure Prevention | Time Limit
on Process Execution without Supervision
Withdrawn
SI-13(3)
Predictable Failure Prevention | Manual
Transfer between Components
SI-13(4)
Predictable Failure Prevention | Standby
Component Installation / Notification
SI-13(5)
Predictable Failure Prevention | Failover
Capability
SI-14
Non-Persistence
SI-14(1)
Non-Persistence | Refresh from Trusted
Sources
SI-15
Information Output Filtering

CNSSI No. 1253
D-35
ID
TITLE
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
L
M
H
L
M
H
L
M
H
SI-16
Memory Protection
X
X
SI-17
Fail-Safe Procedures
PM-1
Information Security Program Plan
Deployed organization-wide. Supporting
information security program. Not associated
with security control baselines. Independent of
any impact level.
PM-2
Senior Information Security Officer
PM-3
Information Security Resources
PM-4
Plan of Action and Milestones Process
PM-5
Information System Inventory
PM-6
Information Security Measures of
Performance
PM-7
Enterprise Architecture
PM-8
Critical Infrastructure Plan
PM-9
Risk Management Strategy
PM-10
Security Authorization Process
PM-11
Mission/Business Process Definition
PM-12
Insider Threat Program
PM-13
Information Security Workforce
PM-14
Testing, Training, and Monitoring
PM-15
Contacts with Security Groups and
Associations
PM-16
Threat Awareness Program
D.2 ADDITIONAL SECURITY CONTROL INFORMATION
Table D-2 includes additional information about the NIST SP 800-53 security controls, including
confidentiality, integrity, and availability associations, justifications for inclusion in NSS
baselines, and potentially common/inheritable controls.
Association of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability to NIST Security Controls: The
security objectives of confidentiality, integrity, and availability are defined in 44 United States
Code (U.S.C.), Section 3542. The NIST SP 800-53 control baselines do not characterize security
controls as having relationships with security objectives. Table D-2 associates the security
controls from NIST SP 800-53, Revision 4, Appendix F with the three security objectives. These
associations are a factor in the development of Table D-1 and can be used to inform tailoring
decisions.
The primary approach and assumptions for security control associations are:
Each control and/or enhancement is allocated based on whether or not the security
objective(s) are the primary focus of the control and/or enhancement. If a security
objective is only indirectly affected by a control and/or enhancement, it is not associated
with that control and/or enhancement.

CNSSI No. 1253
D-36
The first control in each family covers policy and procedures for the entire family and in
most instances they are allocated to all security objectives (confidentiality, integrity, and
availability).
The confidentiality and integrity objectives are largely focused on reading and writing
(disclosure and modification).
Cryptographic methods provide the ability to address disclosure (by encrypting
information) and integrity (through the use of hashes and encrypted hashes). Therefore,
the controls that address the use of cryptographic methods are typically allocated to
confidentiality and integrity.
The integrity objective is also concerned with the correctness of actions.
The availability objective is primarily concerned with survivability and ensuring that the
resources are there when needed.
The availability objective is also concerned with consequence management and
countering certain activities aimed at denial of service.
Justification for NSS Baselines: Controls selected to address the assumptions for NSS are each
associated with a unique justification. Below is the summary of all justifications contained in
Table D-2.
Insider Threat: This control helps to counter/mitigate insider threats that exist within
NSS organizations.
APT: This control helps to counter/mitigate APTs that are targeting NSS and may
already exist within NSS organizations.
NSS Best Practice: This control supports additional best practices beyond those
addressed in the NIST baselines and is necessary to protect national security systems.
Issuance: [Issuance]: This control supports current and draft CNSS issuances that have
technical policy statements.
In support of and/or consistent with [Control(s)]: This control supports and/or is
consistent with other controls and control enhancements in NSS baselines.
NIST Assumption [Assumption]: This control further addresses a NIST assumption.
In support of EO [number]: This control supports an Executive Order.
Enables continuous monitoring: This control supports the Senior Information Sharing
and Safeguarding Steering Committee focus area of continuous monitoring.
Best Practice: This control supports industry or general best security practices (these
controls will be recommended to NIST for inclusion in the baselines).
Potentially Common/Inheritable Controls: The manner in which some controls are articulated in
the control statements or supplemental guidance implies a potential for implementation as a
common control. Table D-2 identifies security controls that may be potentially implemented as
common controls. The final determination of which controls will be implemented as common
controls will vary depending on the organization, mission/business process, or information
system and its intended environment/deployment. The common controls identified in Table D-2
are based on the following assumptions:

CNSSI No. 1253
D-37
Common controls may be allocated at the organization, mission/business process, or
information system level.
Organizations have staff assigned to develop policies and procedures for the entire
organization.
Organizations have established services (e.g. enterprise, local) that implement technical
security controls other information systems can inherit.
Information systems are located in physical facilities that provide physical security
services (e.g., guns, gates, and guards, climate control, fire suppression).
Authorization boundaries have been established for controlled interfaces that do not
include the interconnected information systems.
A single authorization boundary will be established for a cloud-based enterprise.
Authorization boundaries are established for some large information technology services
such as Microsoft Windows domains that include all the information systems that are
managed within the domain. While some information technology components within a
Microsoft Windows domain can rely on other information technology components within
the Microsoft Windows domain to satisfy some controls in a manner similar to
inheritance, that distinction will be addressed in security control traceability matrices
(SCTMs), rather than being described as commonly provided and inherited security
controls.
Table D-2: Additional Security Control Information
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
AC-1
X
X
X
X
AC-2
X
X
AC-2(1)
X
X
X
AC-2(2)
X
X
X
AC-2(3)
X
X
X
AC-2(4)
X
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015.
X
AC-2(5)
X
X
X
Best Practice. Insider Threat.
X
AC-2(6)
X
X
AC-2(7)
X
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015.
AC-2(8)
X
X
AC-2(9)
X
X
Insider Threat.
X
AC-2(10)
X
X
Insider Threat.
AC-2(11)
X
X
AC-2(12)
X
X
Insider Threat.
X
AC-2(13)
X
X
Insider Threat.
AC-3
X
X
AC-3(1)
Withdrawn
AC-3(2)
X
X
AC-3(3)
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-38
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
AC-3(4)
X
X
NIST Assumption: Some user data/information in
organizational information systems is not shareable
with other users who have authorized access to the
same systems.
AC-3(5)
X
X
AC-3(6)
Withdrawn
AC-3(7)
X
X
AC-3(8)
X
X
AC-3(9)
X
AC-3(10)
X
X
X
AC-4
X
X
X
AC-4(1)
X
X
X
AC-4(2)
X
X
X
AC-4(3)
X
X
X
AC-4(4)
X
X
X
AC-4(5)
X
X
X
AC-4(6)
X
X
X
AC-4(7)
X
X
X
AC-4(8)
X
X
X
AC-4(9)
X
X
AC-4(10)
X
X
X
AC-4(11)
X
X
X
AC-4(12)
X
X
X
AC-4(13)
X
X
X
AC-4(14)
X
X
X
AC-4(15)
X
X
X
AC-4(16)
Withdrawn
AC-4(17)
X
X
X
AC-4(18)
X
AC-4(19)
X
X
X
AC-4(20)
X
X
X
AC-4(21)
X
X
X
AC-4(22)
X
X
X
AC-5
X
X
Insider Threat.
AC-6
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice. In support of
and/or consistent with CM-5(5).
AC-6(1)
X
X
Insider Threat.
AC-6(2)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
AC-6(3)
X
X
AC-6(4)
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-39
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
AC-6(5)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
X
AC-6(6)
X
X
X
AC-6(7)
X
X
Insider Threat.
AC-6(8)
X
X
APT. NSS Best Practice.
AC-6(9)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
AC-6(10)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
AC-7
X
X
X
AC-7(1)
Withdrawn
AC-7(2)
X
AC-8
X
X
X
AC-9
X
AC-9(1)
X
AC-9(2)
X
AC-9(3)
X
AC-9(4)
X
AC-10
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
AC-11
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
AC-11(1)
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
AC-12
X
X
AC-12(1)
X
X
NSS Best Practice. NIST Assumption: Some user
data/information in organizational information
systems is not shareable with other users who have
authorized access to the same systems.
AC-13
Withdrawn
AC-14
X
X
AC-14(1)
Withdrawn
AC-15
Withdrawn
AC-16
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
AC-16(1)
X
X
AC-16(2)
X
AC-16(3)
X
AC-16(4)
X
X
AC-16(5)
X
AC-16(6)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
AC-16(7)
X
X
AC-16(8)
X
AC-16(9)
X
X
AC-
16(10)
X
X
AC-17
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-40
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
AC-17(1)
X
X
Insider Threat.
X
AC-17(2)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
AC-17(3)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
AC-17(4)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
AC-17(5)
Withdrawn
AC-17(6)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
AC-17(7)
Withdrawn
AC-17(8)
Withdrawn
AC-17(9)
X
X
APT. NSS Best Practice. NIST Assumption: Some
user data/information in organizational information
systems is not shareable with other users who have
authorized access to the same systems.
X
AC-18
X
X
X
AC-18(1)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
AC-18(2)
Withdrawn
AC-18(3)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
AC-18(4)
X
X
NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
X
AC-18(5)
X
X
X
AC-19
X
X
AC-19(1)
Withdrawn
AC-19(2)
Withdrawn
AC-19(3)
Withdrawn
AC-19(4)
X
X
AC-19(5)
X
X
AC-20
X
X
X
AC-20(1)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
AC-20(2)
X
Insider Threat. APT.
X
AC-20(3)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
AC-20(4)
X
X
AC-21
X
AC-21(1)
X
AC-21(2)
X
AC-22
X
X
AC-23
X
Insider Threat.
X
AC-24
X
X
AC-24(1)
X
X
AC-24(2)
X
X
AC-25
X
X
AT-1
X
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-41
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
AT-2
X
X
X
X
AT-2(1)
X
X
X
X
AT-2(2)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice. In support of
and/or consistent with CM-5(5).
X
AT-3
X
X
X
X
AT-3(1)
X
X
AT-3(2)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
X
AT-3(3)
X
X
X
X
AT-3(4)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
X
AT-4
X
X
X
X
AT-5
Withdrawn
AU-1
X
X
X
X
AU-2
X
X
AU-2(1)
Withdrawn
AU-2(2)
Withdrawn
AU-2(3)
X
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSD No. 504, CNSSI
No. 1015
X
AU-2(4)
Withdrawn
AU-3
X
X
AU-3(1)
X
X
Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
AU-3(2)
X
X
X
AU-4
X
AU-4(1)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
AU-5
X
AU-5(1)
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice. Issuance: CNSSI
No. 1015
AU-5(2)
X
AU-5(3)
X
AU-5(4)
X
X
AU-6
X
X
X
AU-6(1)
X
X
Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
X
AU-6(2)
Withdrawn
AU-6(3)
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
X
AU-6(4)
X
X
Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
AU-6(5)
X
X
X
AU-6(6)
X
X
X
AU-6(7)
X
X
AU-6(8)
X
X
AU-6(9)
X
X
X
AU-
X
X
Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015

CNSSI No. 1253
D-42
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
6(10)
AU-7
X
X
X
AU-7(1)
X
X
X
AU-7(2)
X
X
AU-8
X
AU-8(1)
X
NSS Best Practice. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
AU-8(2)
X
AU-9
X
X
X
AU-9(1)
X
AU-9(2)
X
AU-9(3)
X
AU-9(4)
X
X
Insider Threat.
X
AU-9(5)
X
X
AU-9(6)
X
AU-10
X
Insider Threat.
AU-
10(1)
X
AU-
10(2)
X
AU-
10(3)
X
AU-
10(4)
X
AU-10(5)
Withdrawn
AU-11
X
X
AU-
11(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
AU-12
X
X
AU-
12(1)
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015
AU-
12(2)
X
AU-
12(3)
X
X
NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
AU-13
X
X
AU-
13(1)
X
AU-
13(2)
X
AU-14
X
X
Insider Threat.
AU-
14(1)
X
X
Insider Threat.

CNSSI No. 1253
D-43
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
AU-
14(2)
X
X
Insider Threat.
AU-
14(3)
X
Insider Threat.
AU-15
X
AU-16
X
X
X
AU-
16(1)
X
AU-
16(2)
X
X
CA-1
X
X
X
X
CA-2
X
X
X
X
CA-2(1)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
X
CA-2(2)
X
X
X
X
CA-2(3)
X
X
X
X
CA-3
X
X
CA-3(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
CA-3(2)
X
X
CA-3(3)
X
X
CA-3(4)
X
X
CA-3(5)
X
X
APT.
CA-4
Withdrawn
CA-5
X
X
X
CA-5(1)
X
X
X
CA-6
X
X
X
CA-7
X
X
X
CA-7(1)
X
X
X
X
CA-7(2)
Withdrawn
CA-7(3)
X
X
X
CA-8
X
CA-8(1)
X
CA-8(2)
X
CA-9
X
X
X
CA-9(1)
X
X
CM-1
X
X
X
CM-2
X
CM-2(1)
X
Enables continuous monitoring. Insider Threat.
X
CM-2(2)
X
CM-2(3)
X
CM-2(4)
Withdrawn
CM-2(5)
Withdrawn

CNSSI No. 1253
D-44
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
CM-2(6)
X
CM-2(7)
X
CM-3
X
Enables continuous monitoring. Insider Threat.
X
CM-3(1)
X
X
CM-3(2)
X
CM-3(3)
X
CM-3(4)
X
NSS Best Practice. In support of and/or consistent
with CM-3.
X
CM-3(5)
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 508 (draft).
CM-3(6)
X
Insider Threat.
CM-4
X
X
CM-4(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
CM-4(2)
X
CM-5
X
Insider Threat.
CM-5(1)
X
Insider Threat.
CM-5(2)
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSD No. 508 (draft).
CM-5(3)
X
CM-5(4)
X
CM-5(5)
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice. In support of
and/or consistent with AC-6.
X
CM-5(6)
X
Insider Threat. APT.
X
CM-5(7)
Withdrawn
CM-6
X
X
CM-6(1)
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015.
X
CM-6(2)
X
CM-6(3)
Withdrawn
CM-6(4)
Withdrawn
CM-7
X
X
CM-7(1)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
CM-7(2)
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
CM-7(3)
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
X
CM-7(4)
X
X
This control enhancement is not needed for NSS
since this Instruction prescribes whitelisting, CM-
7(5), at the moderate level for integrity which is
more stringent.
X
CM-7(5)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT. Issuance: CNSSP No. 26
X
CM-8
X
X
CM-8(1)
X
CM-8(2)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
CM-8(3)
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-45
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
CM-8(4)
X
X
X
CM-8(5)
X
X
CM-8(6)
X
X
CM-8(7)
X
X
CM-8(8)
X
X
CM-8(9)
X
X
CM-9
X
In support of and/or consistent with the control
allocations for the CM family.
CM-9(1)
X
X
CM-10
X
X
CM-
10(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
CM-11
X
X
X
CM-
11(1)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
CM-
11(2)
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
CP-1
X
X
X
X
CP-2
X
CP-2(1)
X
CP-2(2)
X
X
CP-2(3)
X
X
CP-2(4)
X
X
CP-2(5)
X
X
CP-2(6)
X
X
CP-2(7)
X
CP-2(8)
X
CP-3
X
CP-3(1)
X
CP-3(2)
X
CP-4
X
CP-4(1)
X
CP-4(2)
X
CP-4(3)
X
CP-4(4)
X
CP-5
Withdrawn
CP-6
X
X
CP-6(1)
X
X
CP-6(2)
X
X
CP-6(3)
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-46
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
CP-7
X
X
X
X
CP-7(1)
X
X
CP-7(2)
X
X
CP-7(3)
X
X
CP-7(4)
X
X
CP-7(5)
Withdrawn
CP-7(6)
X
X
CP-8
X
X
CP-8(1)
X
X
CP-8(2)
X
X
CP-8(3)
X
X
CP-8(4)
X
X
CP-8(5)
X
Best Practice.
CP-9
X
X
X
CP-9(1)
X
X
CP-9(2)
X
CP-9(3)
X
X
CP-9(4)
Withdrawn
CP-9(5)
X
In support of and/or consistent with CP-6.
CP-9(6)
X
CP-9(7)
X
CP-10
X
X
CP-10(1)
Withdrawn
CP-10(2)
X
X
CP-10(3)
Withdrawn
CP-10(4)
X
X
CP-10(5)
Withdrawn
CP-10(6)
X
X
CP-11
X
CP-12
X
X
CP-13
X
IA-1
X
X
X
IA-2
X
X
IA-2(1)
X
X
IA-2(2)
X
X
Issuance: CNSSP No. 25
IA-2(3)
X
X
IA-2(4)
X
X
Issuance: CNSSP No. 25
IA-2(5)
X
X
Insider Threat.
IA-2(6)
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-47
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
IA-2(7)
X
X
IA-2(8)
X
X
APT.
IA-2(9)
X
X
APT.
IA-2(10)
X
IA-2(11)
X
X
APT.
IA-2(12)
X
X
IA-2(13)
X
X
IA-3
X
X
APT. Insider Threat.
IA-3(1)
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSP No. 17
IA-3(2)
Withdrawn
IA-3(3)
X
X
X
IA-3(4)
X
X
IA-4
X
X
X
IA-4(1)
X
X
IA-4(2)
X
IA-4(3)
X
X
IA-4(4)
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
X
IA-4(5)
X
X
IA-4(6)
X
X
IA-4(7)
X
X
IA-5
X
X
X
IA-5(1)
X
X
IA-5(2)
X
X
IA-5(3)
X
X
IA-5(4)
X
X
APT. NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
IA-5(5)
X
X
IA-5(6)
X
X
X
IA-5(7)
X
NSS Best Practice.
IA-5(8)
X
X
APT. NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
X
IA-5(9)
X
X
IA-5(10)
X
IA-5(11)
X
IA-5(12)
X
IA-5(13)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
IA-5(14)
X
X
Issuance: CNSSP No. 25
X
IA-5(15)
X
IA-6
X
IA-7
X
X
IA-8
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-48
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
IA-8(1)
X
X
IA-8(2)
X
IA-8(3)
X
IA-8(4)
X
IA-8(5)
X
X
IA-9
X
X
IA-9(1)
X
X
IA-9(2)
X
X
IA-10
X
X
APT.
IA-11
X
X
APT.
IR-1
X
X
X
X
IR-2
X
X
X
IR-2(1)
X
X
X
IR-2(2)
X
X
IR-3
X
X
X
In support of and/or consistent with IR-1.
IR-3(1)
X
X
X
IR-3(2)
X
X
X
IR-4
X
X
X
X
IR-4(1)
X
X
X
X
IR-4(2)
X
X
X
IR-4(3)
X
X
X
In support of EO 13587. APT.
IR-4(4)
X
X
X
In support of EO 13587. APT. In support of and/or
consistent with IR-5 and IR-6.
X
IR-4(5)
X
X
IR-4(6)
X
X
X
In support of EO 13587. Insider Threat. Issuance:
CNSSD No. 504.
IR-4(7)
X
X
X
In support of EO 13587. Insider Threat. Issuance:
CNSSD No. 504.
IR-4(8)
X
X
X
In support of EO 13587. APT. Insider Threat. In
support of and/or consistent with IR-4(4).
IR-4(9)
X
X
X
IR-4(10)
X
X
X
IR-5
X
X
X
X
IR-5(1)
X
X
X
X
IR-6
X
X
X
X
IR-6(1)
X
X
X
X
IR-6(2)
X
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. In support of and/or consistent
with IR-4(4).
X
IR-6(3)
X
X
X
IR-7
X
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-49
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
IR-7(1)
X
X
X
X
IR-7(2)
X
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. In support of and/or consistent
with IR-4(4).
X
IR-8
X
X
X
X
IR-9
X
NSS Best Practice.
IR-9(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
IR-9(2)
X
NSS Best Practice.
IR-9(3)
X
NSS Best Practice.
IR-9(4)
X
NSS Best Practice.
IR-10
X
X
X
APT. NSS Best Practice.
MA-1
X
X
X
X
MA-2
X
X
X
MA-2(1)
Withdrawn
MA-2(2)
X
X
X
MA-3
X
APT. Insider Threat.
X
MA-3(1)
X
X
MA-3(2)
X
APT. Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSP No. 26
X
MA-3(3)
X
NSS Best Practice.
MA-3(4)
X
MA-4
X
MA-4(1)
X
NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
X
MA-4(2)
X
MA-4(3)
X
X
APT. NSS Best Practice.
MA-4(4)
X
X
MA-4(5)
X
X
MA-4(6)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
MA-4(7)
X
NSS Best Practice.
MA-5
X
X
X
MA-5(1)
X
X
X
MA-5(2)
X
X
X
X
MA-5(3)
X
X
X
X
MA-5(4)
X
X
X
MA-5(5)
X
X
X
MA-6
X
MA-6(1)
X
MA-6(2)
X
MA-6(3)
X
MP-1
X
X
X
MP-2
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-50
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
MP-2(1)
Withdrawn
MP-2(2)
Withdrawn
MP-3
X
MP-4
X
X
MP-4(1)
Withdrawn
MP-4(2)
X
X
MP-5
X
X
X
MP-5(1)
Withdrawn
MP-5(2)
Withdrawn
MP-5(3)
X
X
X
MP-5(4)
X
X
MP-6
X
X
MP-6(1)
X
X
MP-6(2)
X
X
MP-6(3)
X
MP-6(4)
Withdrawn
MP-6(5)
Withdrawn
MP-6(6)
Withdrawn
MP-6(7)
X
MP-6(8)
X
MP-7
X
X
MP-7(1)
X
APT. Issuance: CNSSP No. 26. NSS Best Practice.
MP-7(2)
X
MP-8
X
MP-8(1)
X
MP-8(2)
X
MP-8(3)
X
MP-8(4)
X
PE-1
X
X
X
X
PE-2
X
X
X
X
PE-2(1)
X
X
X
X
PE-2(2)
X
X
PE-2(3)
X
X
PE-3
X
X
X
X
PE-3(1)
X
X
NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
X
PE-3(2)
X
X
PE-3(3)
X
X
X
PE-3(4)
X
X
PE-3(5)
X
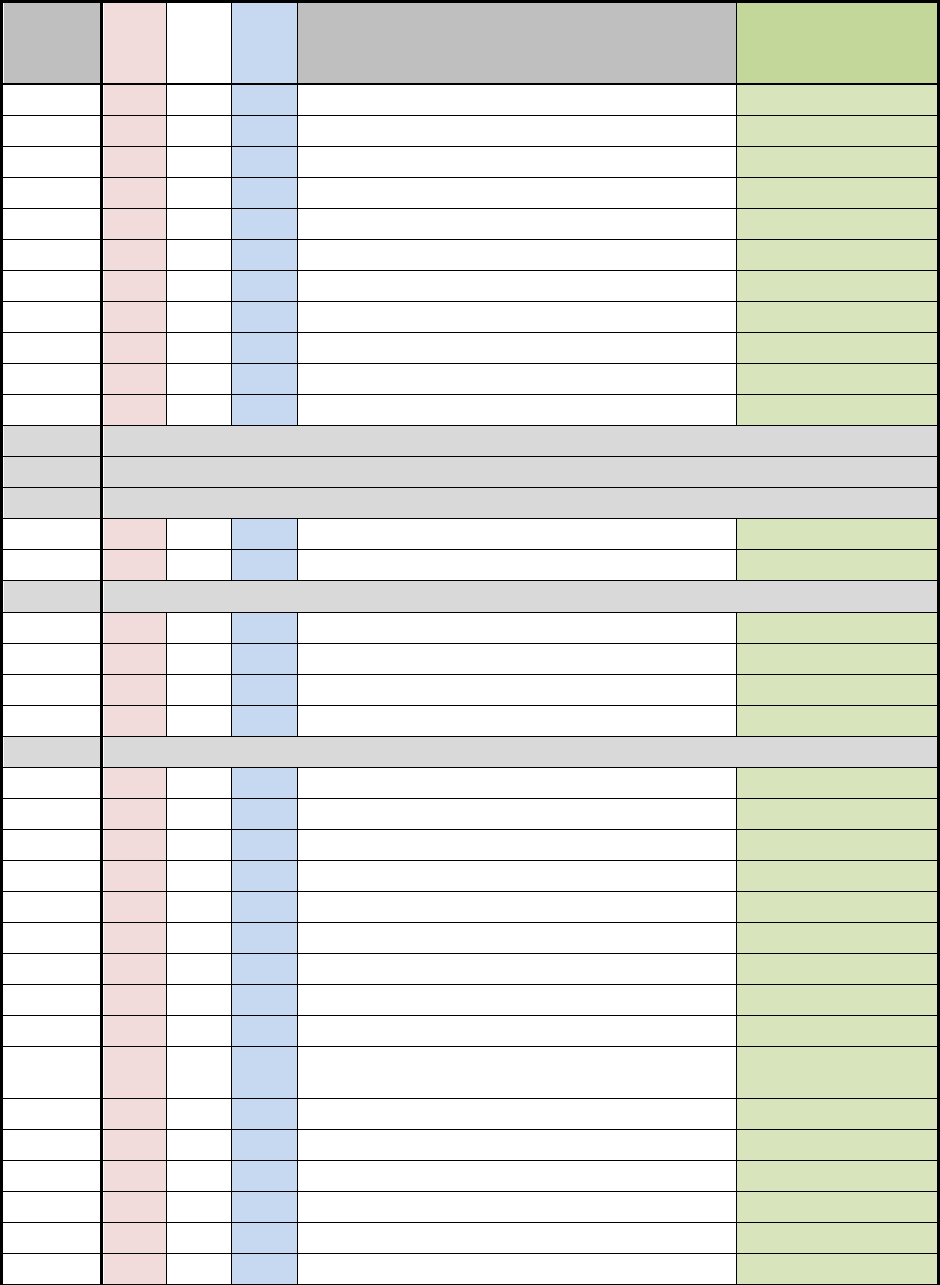
CNSSI No. 1253
D-51
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
PE-3(6)
X
X
PE-4
X
X
X
PE-5
X
PE-5(1)
X
PE-5(2)
X
PE-5(3)
X
PE-6
X
X
X
PE-6(1)
X
X
X
PE-6(2)
X
X
X
PE-6(3)
X
X
X
PE-6(4)
X
X
X
PE-7
Withdrawn
PE-7(1)
Withdrawn
PE-7(2)
Withdrawn
PE-8
X
X
X
X
PE-8(1)
X
X
PE-8(2)
Withdrawn
PE-9
X
X
PE-9(1)
X
PE-9(2)
X
X
PE-10
X
X
PE-10(1)
Withdrawn
PE-11
X
PE-11(1)
X
X
PE-11(2)
X
X
PE-12
X
X
PE-12(1)
X
X
PE-13
X
X
PE-13(1)
X
X
PE-13(2)
X
X
PE-13(3)
X
X
PE-13(4)
X
NIST Assumption: Information systems are located
in physical facilities. Best Practice.
X
PE-14
X
X
PE-14(1)
X
X
PE-14(2)
X
X
PE-15
X
X
PE-15(1)
X
PE-16
X
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-52
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
PE-17
X
X
X
PE-18
X
X
PE-18(1)
X
X
PE-19
X
PE-19(1)
X
PE-20
X
PL-1
X
X
X
X
PL-2
X
X
X
PL-2(1)
Withdrawn
PL-2(2)
Withdrawn
PL-2(3)
X
X
X
PL-3
Withdrawn
PL-4
X
X
X
PL-4(1)
X
X
PL-5
Withdrawn
PL-6
Withdrawn
PL-7
X
X
X
PL-8
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
PL-8(1)
X
X
X
APT.
PL-8(2)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
PL-9
X
X
X
X
PS-1
X
X
X
X
PS-2
X
X
X
X
PS-3
X
X
PS-3(1)
X
PS-3(2)
X
PS-3(3)
X
PS-4
X
X
X
PS-4(1)
X
Best Practice.
PS-4(2)
X
X
X
PS-5
X
X
X
PS-6
X
X
X
PS-6(1)
Withdrawn
PS-6(2)
X
X
PS-6(3)
X
Best Practice.
PS-7
X
X
X
PS-8
X
X
X
X
RA-1
X
X
X
X
RA-2
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-53
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
RA-3
X
X
X
RA-4
Withdrawn
RA-5
X
X
X
RA-5(1)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. APT. NSS Best Practice.
RA-5(2)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
RA-5(3)
X
X
X
X
RA-5(4)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
RA-5(5)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. APT.
RA-5(6)
X
X
X
RA-5(7)
Withdrawn
RA-5(8)
X
X
X
RA-5(9)
Withdrawn
RA-5(10)
X
X
X
APT.
RA-6
X
X
X
SA-1
X
X
X
X
SA-2
X
X
X
SA-3
X
X
X
SA-4
X
X
X
SA-4(1)
X
X
X
X
SA-4(2)
X
X
X
X
SA-4(3)
X
NSS Best Practice. Issuance: CNSSD No. 505.
X
SA-4(4)
Withdrawn
SA-4(5)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SA-4(6)
X
X
SA-4(7)
X
Issuance: CNSSP No. 11
SA-4(8)
X
X
X
SA-4(9)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SA-4(10)
X
X
SA-5
X
X
X
SA-5(1)
Withdrawn
SA-5(2)
Withdrawn
SA-5(3)
Withdrawn
SA-5(4)
Withdrawn
SA-5(5)
Withdrawn
SA-6
Withdrawn
SA-6(1)
Withdrawn
SA-7
Withdrawn
SA-8
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-54
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SA-9
X
X
X
SA-9(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SA-9(2)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SA-9(3)
X
SA-9(4)
X
X
X
SA-9(5)
X
X
X
SA-10
X
In support of and/or consistent with desired
allocation of SA-10(1).
SA-10(1)
X
APT.
SA-10(2)
X
SA-10(3)
X
SA-10(4)
X
SA-10(5)
X
SA-10(6)
X
SA-11
X
X
X
SA-11(1)
X
X
X
SA-11(2)
X
X
X
SA-11(3)
X
X
X
SA-11(4)
X
X
X
SA-11(5)
X
X
X
SA-11(6)
X
X
X
SA-11(7)
X
X
X
SA-11(8)
X
X
X
SA-12
X
X
X
APT. Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
X
SA-12(1)
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-12(2)
X
X
X
X
SA-12(3)
Withdrawn
SA-12(4)
Withdrawn
SA-12(5)
X
X
X
APT, Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-12(6)
Withdrawn
SA-12(7)
X
X
X
SA-12(8)
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-12(9)
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-
12(10)
X
SA-
12(11)
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-
12(12)
X
X
X
SA-
12(13)
X
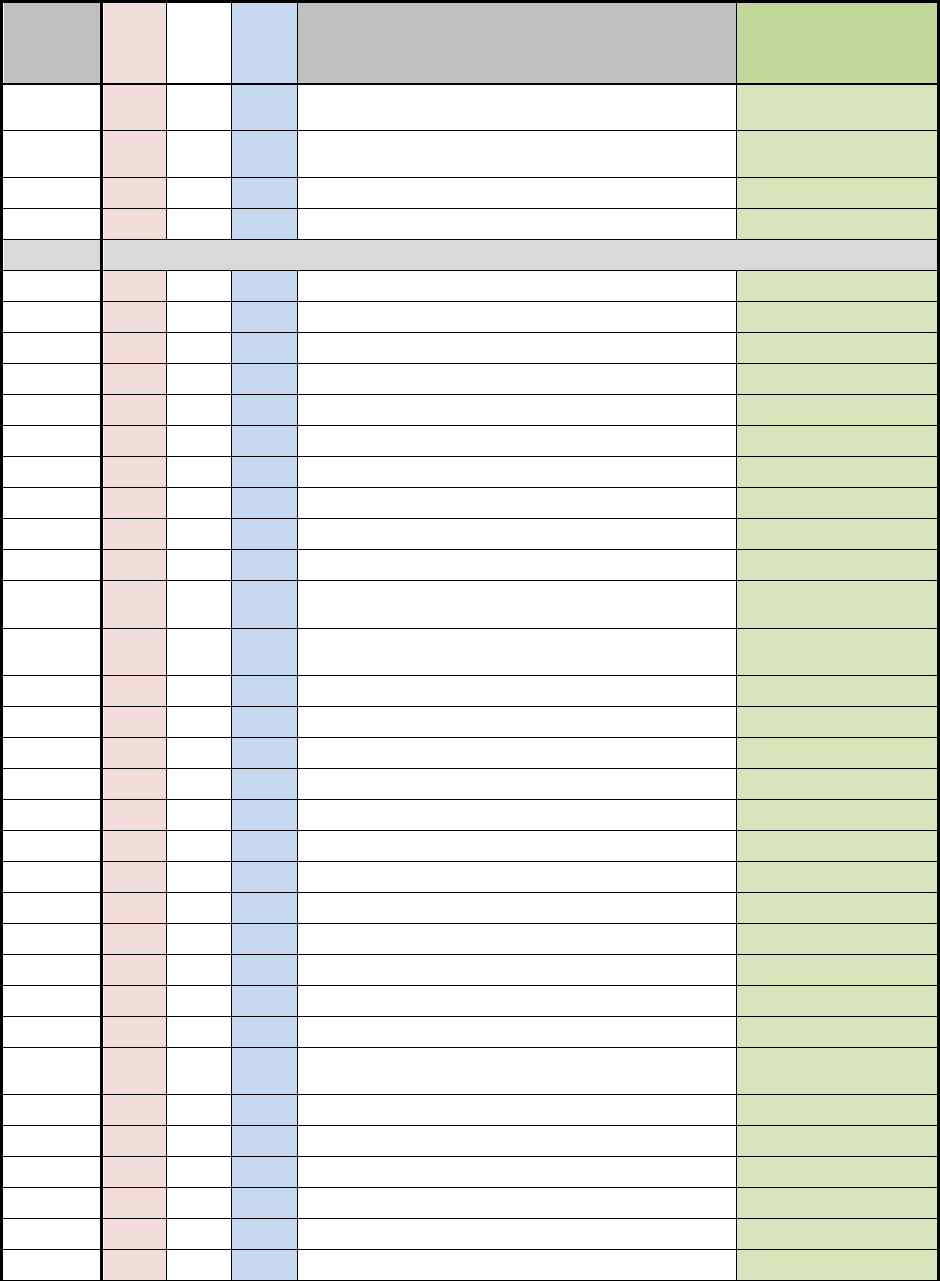
CNSSI No. 1253
D-55
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SA-
12(14)
X
SA-
12(15)
X
X
X
SA-13
X
SA-14
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-14(1)
Withdrawn
SA-15
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SA-15(1)
X
X
X
SA-15(2)
X
SA-15(3)
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-15(4)
X
X
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-15(5)
X
SA-15(6)
X
X
X
SA-15(7)
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505
SA-15(8)
X
SA-15(9)
X
NSS Best Practice.
SA-
15(10)
X
X
X
SA-
15(11)
X
SA-16
X
X
X
SA-17
X
X
X
SA-17(1)
X
X
X
SA-17(2)
X
X
X
SA-17(3)
X
X
X
SA-17(4)
X
X
X
SA-17(5)
X
X
X
SA-17(6)
X
X
X
SA-17(7)
X
X
SA-18
X
SA-18(1)
X
SA-18(2)
X
SA-19
X
Issuance: CNSSD No. 505. NSS Best Practice.
APT.
SA-19(1)
X
SA-19(2)
X
SA-19(3)
X
X
SA-19(4)
X
SA-20
X
SA-21
X
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-56
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SA-21(1)
X
X
X
SA-22
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SA-22(1)
X
SC-1
X
X
X
X
SC-2
X
X
SC-2(1)
X
X
SC-3
X
X
X
SC-3(1)
X
X
SC-3(2)
X
X
SC-3(3)
X
X
SC-3(4)
X
X
SC-3(5)
X
X
SC-4
X
SC-4(1)
Withdrawn
SC-4(2)
X
SC-5
X
SC-5(1)
X
Insider Threat.
SC-5(2)
X
NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat.
SC-5(3)
X
In support of and/or consistent with allocations of
the control and its enhancements.
SC-6
X
SC-7
X
X
X
SC-7(1)
Withdrawn
SC-7(2)
Withdrawn
SC-7(3)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-7(4)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-7(5)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-7(6)
Withdrawn
SC-7(7)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-7(8)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SC-7(9)
X
Insider Threat. In support of and/or consistent with
SC-5(1).
SC-7(10)
X
APT. Insider Threat.
SC-7(11)
X
NSS Best Practice. Best Practice.
SC-7(12)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice. Best Practice.
SC-7(13)
X
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
X
SC-7(14)
X
X
NSS Best Practice. Best Practice.
SC-7(15)
X
X
SC-7(16)
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-57
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SC-7(17)
X
SC-7(18)
X
X
X
SC-7(19)
X
X
SC-7(20)
X
SC-7(21)
X
X
SC-7(22)
X
X
SC-7(23)
X
SC-8
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-8(1)
X
X
In support of and/or consistent with SC-8.
SC-8(2)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-8(3)
X
SC-8(4)
X
SC-9
Withdrawn
SC-9(1)
Withdrawn
SC-9(2)
Withdrawn
SC-10
X
X
SC-11
X
SC-11(1)
X
SC-12
X
X
X
SC-12(1)
X
SC-12(2)
X
X
SC-12(3)
X
X
SC-12(4)
Withdrawn
SC-12(5)
Withdrawn
SC-13
X
X
SC-13(1)
Withdrawn
SC-13(2)
Withdrawn
SC-13(3)
Withdrawn
SC-13(4)
Withdrawn
SC-14
Withdrawn
SC-15
X
SC-15(1)
X
SC-15(2)
Withdrawn
SC-15(3)
X
SC-15(4)
X
SC-16
X
X
SC-16(1)
X
SC-17
X
X
Issuance: CNSSP No. 25
X
SC-18
X
NSS Best Practice.
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-58
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SC-18(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SC-18(2)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SC-18(3)
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-18(4)
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-18(5)
X
X
SC-19
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SC-20
X
SC-20(1)
Withdrawn
SC-20(2)
X
SC-21
X
SC-21(1)
Withdrawn
SC-22
X
X
X
SC-23
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
SC-23(1)
X
APT.
SC-23(2)
Withdrawn
SC-23(3)
X
APT.
SC-23(4)
Withdrawn
SC-23(5)
X
APT. Issuance: CNSSP No. 25
SC-24
X
X
SC-25
X
SC-26
X
SC-26(1)
Withdrawn
SC-27
X
SC-28
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-28(1)
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SC-28(2)
X
SC-29
X
X
X
SC-29(1)
X
X
X
SC-30
X
X
X
SC-30(1)
Withdrawn
SC-30(2)
X
X
X
SC-30(3)
X
X
X
SC-30(4)
X
X
X
SC-30(5)
X
X
X
SC-31
X
SC-31(1)
X
SC-31(2)
X
SC-31(3)
X
SC-32
X
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-59
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SC-33
Withdrawn
SC-34
X
SC-34(1)
X
SC-34(2)
X
SC-34(3)
X
SC-35
X
SC-36
X
X
SC-36(1)
X
X
X
SC-37
X
X
X
SC-37(1)
X
X
SC-38
X
X
X
Insider Threat. APT. NSS Best Practice.
SC-39
X
X
SC-39(1)
X
X
SC-39(2)
X
X
SC-40
X
X
X
SC-40(1)
X
SC-40(2)
X
SC-40(3)
X
SC-40(4)
X
SC-41
X
X
SC-42
X
SC-42(1)
X
SC-42(2)
X
SC-42(3)
X
SC-43
X
X
X
X
SC-44
X
SI-1
X
X
X
X
SI-2
X
X
SI-2(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
SI-2(2)
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
SI-2(3)
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
X
SI-2(4)
Withdrawn
SI-2(5)
X
SI-2(6)
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
SI-3
X
X
SI-3(1)
X
NSS Best Practice.
X
SI-3(2)
X
NSS Best Practice.
SI-3(3)
Withdrawn
SI-3(4)
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-60
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SI-3(5)
Withdrawn
SI-3(6)
X
SI-3(7)
X
SI-3(8)
X
SI-3(9)
X
SI-3(10)
X
APT.
SI-4
X
X
X
SI-4(1)
X
X
X
APT.
SI-4(2)
X
X
X
SI-4(3)
X
X
SI-4(4)
X
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice. In support
of and/or consistent with SI-4(11).
SI-4(5)
X
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
SI-4(6)
Withdrawn
SI-4(7)
X
X
X
SI-4(8)
Withdrawn
SI-4(9)
X
X
X
SI-4(10)
X
X
X
APT. Insider Threat.
X
SI-4(11)
X
X
X
APT. Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice. In support
of and/or consistent with SI-4(4).
SI-4(12)
X
X
X
Insider Threat.
SI-4(13)
X
X
X
SI-4(14)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
SI-4(15)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SI-4(16)
X
X
X
Insider Threat. Issuance: CNSSI No. 1015. In
support of and/or consistent with SI-4(1).
SI-4(17)
X
X
X
X
SI-4(18)
X
SI-4(19)
X
X
X
Insider Threat.
SI-4(20)
X
X
X
Insider Threat.
SI-4(21)
X
X
X
SI-4(22)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice.
SI-4(23)
X
X
X
NSS Best Practice. Insider Threat. APT.
SI-4(24)
X
X
X
SI-5
X
X
SI-5(1)
X
X
SI-6
X
SI-6(1)
Withdrawn
SI-6(2)
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-61
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SI-6(3)
X
NSS Best Practice. In support of and/or consistent
with SI-6.
X
SI-7
X
X
SI-7(1)
X
SI-7(2)
X
SI-7(3)
X
SI-7(4)
Withdrawn
SI-7(5)
X
SI-7(6)
X
SI-7(7)
X
SI-7(8)
X
Insider Threat. NSS Best Practice.
SI-7(9)
X
SI-7(10)
X
SI-7(11)
X
SI-7(12)
X
SI-7(13)
X
SI-7(14)
X
NSS Best Practice.
SI-7(15)
X
SI-7(16)
X
SI-8
X
X
X
SI-8(1)
X
X
X
SI-8(2)
X
X
SI-8(3)
X
X
SI-9
Withdrawn
SI-10
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
SI-10(1)
X
SI-10(2)
X
SI-10(3)
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
SI-10(4)
X
SI-10(5)
X
SI-11
X
NSS Best Practice. APT.
SI-12
X
X
X
SI-13
X
SI-13(1)
X
SI-13(2)
Withdrawn
SI-13(3)
X
SI-13(4)
X
SI-13(5)
X
SI-14
X

CNSSI No. 1253
D-62
ID
C
I
A
Justification for NSS Baseline(s)
Potentially
Common/Inheritable
SI-14(1)
X
SI-15
X
SI-16
X
SI-17
X
PM-1
Common controls deployed organization-wide. Supporting information security program. Not
associated with security control baselines. Independent of any impact level.
PM-2
PM-3
PM-4
PM-5
PM-6
PM-7
PM-8
PM-9
PM-10
PM-11
PM-12
PM-13
PM-14
PM-15
PM-16

CNSSI No. 1253
E-1
APPENDIX E
SECURITY CONTROL PARAMETER VALUES
Table E-1 contains parameter values specified for NSS. These parameter values are minimum
standards for NSS. Any deviations from these values should be documented in the security plan.
If a control or control enhancement does not appear in Table E-1:
It does not have an organizationally defined parameter;
All parameters within a control are not appropriate to define for all NSS at the CNSS
level; or
It was withdrawn from NIST SP 800-53.
Table E-1: Security Control Parameter Values for NSS
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
AC-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all organizations operating NSS.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy
AC-2
a. [Assignment: organization-defined
information system account types]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
e. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
e. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
f. [Assignment: organization-defined procedures
or conditions]
f. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
j. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
j. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
AC-2(2)
[Selection: removes; disables]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period
for each type of account]
Disables
Not to exceed 72 hours.
AC-2(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period].
Not to exceed 90 days.
AC-2(5)
[Assignment: organization-defined time-period
of expected inactivity or description of when to
log out]
At the end of the users standard work period
unless otherwise defined in formal organizational
policy.
AC-2(7)
(c) [Assignment: organization-defined actions
(c) Disables (or revokes) privileged user account.
AC-2(13)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
30 minutes unless otherwise defined in formal
organizational policy.
AC-6(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined security
functions or security-relevant information]
Privileged functions.
AC-6(8)
[Assignment: organization-defined software]
All
AC-7
a. [Assignment: organization-defined number]
3

CNSSI No. 1253
E-2
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
15 minutes
b. [Selection: locks the account/node for an
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
[Assignment: organization-defined delay
algorithm]]
b. locks the account/node for
at least 15 minutes, or until unlocked by an
administrator.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
AC-7(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined mobile
devices]
[Assignment: organization-defined
purging/wiping requirements/techniques]
[Assignment: organization-defined number]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
10
AC-9(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined security-
related characteristics/parameters of the user’s
account]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Since last successful logon
AC-10
[Assignment: organization-defined account
and/or account type]
[Assignment: organization-defined number]
Non-Privileged
maximum of 3
sessions
Privileged
maximum of 3
sessions
AC-11
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
Not to exceed 30 minutes
AC-12(1)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined
information resources]
(a) All
AC-14
a. [Assignment: organization-defined user
actions]
a. No user actions
AC-17(9)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
Low confidentiality or integrity impact:
...30 minutes
Moderate confidentiality or integrity impact:
...20 minutes
High confidentiality or integrity impact:
...10 minutes
AC-18(1)
[Selection (one or more): users; devices]
Both users and devices as appropriate. See
supplemental guidance.
Supplemental Guidance: devices to wireless
networks (e.g., Wi-Fi) and users to enterprise
services.
AC-19(5)
[Selection: full-device encryption; container
encryption]
[Assignment: organization-defined mobile
devices]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
All mobile devices authorized to connect to the
organization's ISs.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-3
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
AC-20(3)
[Selection: restricts; prohibits]
Restricts
AC-22
d. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
d. Quarterly or as new information is posted.
AT-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
AT-2
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organization.
AT-3
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organization.
AT-3(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel or
roles]
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organization policy or when sufficient
changes are made to physical security systems.
AT-3(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel or
roles]
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organization policy or when sufficient
changes are made to physical security systems.
AT-3(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined indicators of
malicious code]
Minimally but not limited to indicators of
potentially malicious code in suspicious email.
AU-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
AU-2
a. [Assignment: organization-defined auditable
events]
a.
1. Authentication events:
(1) Logons (Success/Failure)
(2) Logoffs (Success)
2. File and Objects events:
(1) Create (Success/Failure)
(2) Access (Success/Failure)
(3) Delete (Success/Failure)
(4) Modify (Success/Failure)
(5) Permission Modification
(Success/Failure)
(6) Ownership Modification (Success/Failure)
3. Writes/downloads to external devices/media
(e.g., A-Drive, CD/DVD devices/printers)
(Success/Failure)

CNSSI No. 1253
E-4
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
4. Uploads from external devices (e.g., CD/DVD
drives) (Success/Failure)
5. User and Group Management events:
(1) User add, delete, modify, suspend, lock
(Success/Failure)
(2) Group/Role add, delete, modify
(Success/Failure)
6. Use of Privileged/Special Rights events:
(1) Security or audit policy changes
(Success/Failure)
(2) Configuration changes (Success/Failure)
7. Admin or root-level access (Success/Failure)
8. Privilege/Role escalation (Success/Failure)
9. Audit and log data accesses (Success/Failure)
10. System reboot, restart and shutdown
(Success/Failure)
11. Print to a device (Success/Failure)
12. Print to a file (e.g., pdf format)
(Success/Failure)
13. Application (e.g., Firefox, Internet Explorer,
MS Office Suite, etc.) initialization
(Success/Failure)
14. Export of information (Success/Failure)
include (e.g., to CDRW, thumb drives, or
remote systems)
15. Import of information (Success/Failure)
include (e.g., from CDRW, thumb drives, or
remote systems)
d. [Assignment: organization-defined audited
events (the subset of the auditable events defined
in AU-2 a.) along with the frequency of (or
situation requiring) auditing for each identified
event]
d. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
AU-2(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy
AU-5(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel,
roles, and/or locations]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
[Assignment: organization-defined percentage]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Max of 75%

CNSSI No. 1253
E-5
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
AU-5(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined real-time
period]
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel,
roles, and/or locations]
[Assignment: organization-defined audit failure
events requiring real-time alerts]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Minimally but not limited to: auditing
software/hardware errors; failures in the audit
capturing mechanisms; and audit storage
capacity being reached or exceeded.
AU-6
a. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined inappropriate
or unusual activity]
a. At least weekly (seven days)
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
b. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
AU-8(1)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined authoritative
time source]
(a) At least every 24 hours.
(a) Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
(b) [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
(b) Greater than the organizationally defined
granularity in AU-8.
AU-9(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
a. At least weekly.
AU-9(5)
[Selection (one or more): movement; deletion]
[Assignment: organization-defined audit
information]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Any security related audit information.
AU-11
[Assignment: organization-defined time period
consistent with records retention policy]
A minimum of 5 years for Sensitive
Compartmented Information and Sources And
Methods Intelligence information
AND
A minimum of 1 year for all other information
(Unclassified through Collateral Top Secret).
AU-11(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined measures]
A retention of technology to access audit records
for the duration of the required retention period.
AU-12
a. [Assignment: organization-defined
information system components]
a. All information systems and network
components.
b. Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
b. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
AU-12(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined information
system components]
[Assignment: organization-defined level of
tolerance for relationship between time stamps of
individual records in the audit trail]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
In accordance with tolerance defined in AU-8.
AU-13(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-6
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
CA-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
CA-2
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually, or as stipulated in the
organization's continuous monitoring program.
d. [Assignment: organization-defined individuals
or roles]
d. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
CA-3
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually.
CA-3(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined unclassified,
national security system]
[Assignment: organization-defined boundary
protection device]
All unclassified NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
CA-3(5)
[Selection: allow-all, deny-by-exception; deny-
all, permit-by-exception]
[Assignment: organization-defined information
systems] to connect to external information
systems.
Deny-all, permit-by-exception.
All systems.
CA-5
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least quarterly.
CA-6
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. If the organization and/or system is
adequately covered by a continuous monitoring
program the Security Authorization may be
continuously updated:
If not; at least every three (3) years, when
significant security breaches occur, whenever
there is a significant change to the system, or to
the environment in which the system operates.
CM-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
CM-2(1)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(a) At least annually.
(b) [Assignment organization-defined
circumstances]
(b) Significant or security relevant changes or
security incidents occur.
CM-2(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined previous
versions of baseline configurations of the
information system]
At least two.
CM-3
e. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
e. 1 year or two change cycles of baseline
configurations as defined in CM-2 (3), whichever
is longer.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-7
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
g. [Assignment: organization-defined
configuration change control element (e.g.,
committee, board]
[Selection (one or more):
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined configuration
change conditions]]
g. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
CM-3(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined configuration
change control element]
The configuration change control element
defined in CM-3 g.
Supplemental guidance: The information security
representative shall be a voting member.
CM-3(6)
[Assignment: organization-defined security
safeguards]
All security safeguards that rely on cryptography
CM-5(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined
circumstances]
Every 90 days or more frequently as the
organization defines for high integrity systems
AND at least annually or more frequently as the
organization defines for low integrity and
moderate integrity systems.
When there is an incident or when planned
changes have been performed.
CM-5(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined software and
firmware components]
All digitally signed software and firmware
products.
CM-5(5)
(b) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(b) At least annually.
CM-6
a. [Assignment: organization-defined security
configuration checklists]
a. Organizationally approved guides such as DoD
SRGs, STIGs, or NSA SCGs; if such a reference
document is not available, the following are
acceptable in descending order as available: (1)
Commercially accepted practices (e.g., SANS)
(2) Independent testing results (e.g., ICSA) or (3)
Vendor literature.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined
information system components]
[Assignment: organization-defined operational
requirements]
c. All configurable information system
components.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
CM-6(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined information
system components]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS but minimally for all IA enabled or
related components.
CM-7(1)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(a) At least annually or as system changes or
incidents occur.
(b) [Assignment: organization-defined functions,
(b) All functions, ports, protocols, and services

CNSSI No. 1253
E-8
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
ports, protocols, and services within the
information system deemed to be unnecessary
and/or nonsecure]
within the information system deemed to be
unnecessary and/or nonsecure.
CM-7(4)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined software
programs not authorized to execute on the
information system]
(a) Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
(c) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(c) At least annually.
CM-7(5)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined software
programs authorized to execute on the
information system]
(a) Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
(c) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(c) At least annually.
CM-8
a.4. [Assignment: organization-defined
information deemed necessary to achieve
effective information system component
accountability]
a.4. Minimally but not limited to: hardware
specifications (manufacturer, type, model, serial
number, physical location), software and
software license information, information
system/component owner, and for a networked
component/device, the machine name.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually.
CM-8(3)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(a) Continuously.
(b) [Selection (one or more): disables network
access by such components; isolates the
components; notifies
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel or
roles]]
(b) Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
CM-8(4)
[Selection (one or more): name; position; role]
Minimally position or role.
CM-8(9)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined acquired
information system components]
All acquired information system components.
See supplemental guidance.
Supplemental guidance: this is part of Security
Authorization, "authorization boundary".
CM-11
a. [Assignment: organization-defined policies]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined methods]
b. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. Continuously.
CP-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
CP-2
a.6. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a.6. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-9
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
b. [Assignment: organization-defined key
contingency personnel (identified by name
and/or by role) and organizational elements]
b. Key personnel or roles and organizational
elements identified in the contingency plan.
d. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
d. At least annually unless otherwise defined in
organizational policy.
f. [Assignment: organization-defined key
contingency personnel (identified by name
and/or by role) and organizational elements]
f. Key personnel and .organizational elements
identified in the contingency plan.
CP-2(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
A time period as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-2(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
A time period as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-3
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
a. 10 working days .
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. Annually or as defined in the contingency
plan.
CP-4
a. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined tests]
a. At a frequency as defined in the contingency
plan.
Tests as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-7
a. [Assignment: organization-defined
information system operations]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period
consistent with recovery time and recovery point
objectives]
a. Information system operations as defined in
the contingency plan.
A time period as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-8
[Assignment: organization-defined information
system operations]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
Information system operations as defined in the
contingency plan.
A time period as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-9
a. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency
consistent with recovery time and recovery point
objectives]
a. At least weekly or as defined in the
contingency plan.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency
consistent with recovery time and recovery point
objectives]
b. At least weekly or as defined in the
contingency plan.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency
consistent with recovery time and recovery point
objectives]
c. When created, received, updated, or as defined
in the contingency plan.
CP-9(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least monthly or as defined in the contingency
plan.
CP-9(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined critical
information system software and other security-
related information]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS but as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-9(5)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period
and transfer rate consistent with the recovery
time and recovery point objectives]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS but as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-9(7)
[Assignment: organization-defined backup
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for

CNSSI No. 1253
E-10
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
information]
all NSS, but as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-10(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined restoration
time-periods]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS but as defined in the contingency plan.
CP-11
[Assignment: organization-defined alternative
communications protocols]
Alternate communications protocols as defined
in the contingency plan.
IA-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. Identification and authentication policy
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency];
and
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. Identification and authentication procedures
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
IA-4
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
d.[Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
d. At least a year for individuals, groups, roles
...Not appropriate to define for device identifiers
(e.g., media access control (MAC), Internet
protocol (IP) addresses, or device-unique token
identifiers."
e. [Assignment: organization-defined time period
of inactivity]
e. Not to exceed 35 days for individuals, groups,
roles.
Not appropriate to define for device identifiers
(e.g., media access control (MAC), Internet
protocol (IP) addresses, or device-unique token
identifiers."
IA-5
g. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period by authenticator type]
g. Not to exceed 180 days for passwords; ...Not
appropriate to define at the CNSS level for all
NSS using other authenticator types.
IA-5(1)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined
requirements for case sensitivity, number of
characters, mix of upper-case letters, lower-case
letters, numbers, and special characters,
including minimum requirements for each type]
(a) A case sensitive 12-character mix of upper
case letters, lower case letters, numbers and
special characters in including at least one of
each.
(b) [Assignment: organization-defined number]
(b) 50% of the characters.
(d) [Assignment: organization-defined numbers
for lifetime minimum, lifetime maximum]
d) 24 hours minimum and 180 days maximum.
(e) [Assignment: organization-defined number]
(e) Minimum of 10; (does not apply to one time
use passwords).
IA-5(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined requirements]
Requirements as defined in IA-5 (1).
IA-5(8)
[Assignment: organization-defined security
safeguards]
Precautions including advising users that they
must not use the same password for any of the
following: Domains of differing classification
levels; More than one domain of a classification
level (e.g., internal agency network and
Intelink).; More than one privilege level (e.g.,
user, administrator).

CNSSI No. 1253
E-11
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
IA-5(13)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period].
1 hour.
IR-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
IR-2
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
a. 30 working days.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually.
IR-3
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined tests]
At least annually.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
IR-4(8)
[Assignment: organization-defined external
organizations]
[Assignment: organization-defined incident
information]
The appropriate CIRT/CERT (such as US-
CERT, DoD CERT, IC CERT)
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
IR-6
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
a. 2 hours if not otherwise defined in formal
organizational policy.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined authorities]
b. The appropriate Agency CIRT/CERT (see IR-
4(8)).
IR-8
a.8. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a.8. CISO/SISO if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined incident
response personnel (identified by name and/or by
role) and organizational elements]
b. All personnel with a role or responsibility for
implementing the incident response plan.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually (incorporating lessons
learned from past incidents).
e. [Assignment: organization-defined incident
response personnel (identified by name and/or by
role) and organizational elements]
e. All personnel with a role or responsibility for
implementing the incident response plan.
IR-9(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
Annually.
MA-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
2. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
MA-4(1)
(a) [Assignment: organization-defined audit
events]
(a) As defined in the organizations formal audit
policy (AU-1).
MP-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b. 1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-12
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
MP-2
[Assignment: organization-defined types of
digital and/or non-digital media]
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel or
roles].
All types of digital and/or non-digital media
containing information not cleared for public
release.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
MP-6(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
MP-6(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined
circumstances requiring sanitization of portable
storage devices]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS, however the use of nondestructive
sanitization techniques are for the elimination of
malicious code, not removal of approved
information or software.
MP-8(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined tests]
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PE-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b. 1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PE-2
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually.
PE-6
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined events or
potential indications of events]
b. At least every 90 days if not otherwise defined
in formal organizational policy.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
PE-6(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined operational
areas]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
At least 90 days if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PE-8
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
a. At least one year.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least every 90 days if not otherwise defined
in formal organizational policy.
PE-13(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
60 days.
PE-14
a. [Assignment: organization-defined acceptable
levels]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-13
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. continuously.
PL-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PL-2
b. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
b. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually or when required due to
system changes or modifications.
PL-4
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PL-7
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually or when changes to the
information system or its environment warrant.
PL-8
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually or when changes to the
information system or its environment warrant.
PS-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PS-2
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually or when the position
description is updated or when the position is
vacated.
PS-4
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
a. If voluntary: As soon as possible, not to
exceed 5 working days.
If involuntary: Within same day as termination.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined
information security topics]
c. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
f. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
f. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
As soon as possible, not to exceed 1 working
day.
PS-5
b. [Assignment: organization-defined transfer or
reassignment actions]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period
following the formal transfer action]
b. Reassignment actions to ensure all system
access no longer required (need to know) are
removed or disabled.
b. 10 working days if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
d. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
d. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for

CNSSI No. 1253
E-14
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
all NSS.
PS-6
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy .
c.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
c.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
PS-7
d. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
d. Organizational Security Manager.
As soon as possible, not to exceed 1 working
day.
RA-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
RA-3
b. [Selection: security plan; risk assessment
report;
[Assignment: organization-defined document]]
b. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
d. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
d. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
e. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
e. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
RA-5
a. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency
and/or randomly in accordance with
organization-defined process]
a. At least every 120 days.
d. [Assignment: organization-defined response
times]
d. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
e. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
e. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
RA-5(2)
[Selection (one or more): [Assignment:
organization-defined frequency]; prior to a new
scan; when new vulnerabilities are identified and
reported].
Within 24 hours prior to running scans.
RA-5(5)
[Assignment: organization-identified information
system components]
[Assignment: organization-defined vulnerability
scanning activities]
Authorized vulnerability scanning components.
Authorization by the CISO/SISO or designate.
SA-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b. 1. [Assignment: organization-defined
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in

CNSSI No. 1253
E-15
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
frequency]
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
SA-9(1)
(b) [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles].
(b) Chief Information Officer.
SA-9(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined external
information system services]
All external information systems and services.
SA-12
[Assignment: organization-defined security
safeguards]
Security safeguards in accordance with CNSSD
No. 505, Supply Chain Risk Management.
SC-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
SC-7(4)
(e) [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
(e) At least every 180 days.
SC-7(8)
[Assignment: organization-defined internal
communications traffic]
[Assignment: organization-defined external
networks]
All internal communications traffic that may be
proxied, except traffic specifically exempted by
the Authorizing Official or organizational policy.
All untrusted networks outside the control of the
organization.
SC-7(12)
[Assignment: organization-defined host-based
boundary protection mechanisms]
[Assignment: organization-defined information
system components]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
All system components capable of supporting
host-based boundary protection mechanisms
such as but not limited to servers, workstations,
and those subject to operation outside of the
organizational boundary( i.e., laptops and other
mobile devices).
SC-7(14)
[Assignment: organization-defined managed
interfaces]
Any managed interface that crosses security
domains or connects to an external network; such
as but not limited to: cross domain solutions
(SABI, TSABI), a network boundary with a
WAN, a partner network, or the Internet.
SC-7(19)
[Assignment: organization-defined
communication clients]
All.
SC-8(1)
[Selection (one or more): prevent unauthorized
disclosure of information; detect changes to
information]
[Assignment: organization-defined alternative
physical safeguards].
Prevent unauthorized disclosure of, and detect
changes to, information.
Alternative physical safeguards such as keeping
transmission within physical areas rated IAW the
sensitivity of the information or within a
Protected Distribution System (PDS) when
traversing areas not approved for the sensitivity
of the information.

CNSSI No. 1253
E-16
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
SC-8(2)
[Selection (one or more): confidentiality;
integrity]
Confidentiality and integrity.
SC-10
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
No more than one hour.
SC-11
[Assignment: organization-defined security
functions to include at a minimum, information
system authentication and re-authentication]
Information system authentication and re-
authentication; functions other than the minimum
required are not appropriate to define at the
CNSS level for all NSS.
SC-12
[Assignment: organization-defined requirements
for key generation, distribution, storage, access,
and destruction]
For unclassified NSS, NIST FIPS-compliant;
and/or for classified NSS, see the Classified
Information Overlay; processes/requirements for
key generation, distribution, storage, access, and
destruction.
SC-12(2)
[Selection: NIST FIPS-compliant; NSA-
approved]
NIST FIPS-compliant for unclassified data,
and/or
See Classified Information Overlay for classified
data.
SC-15
a. [Assignment: organization-defined exceptions
where remote activation is to be allowed]
Dedicated VTC suites located in approved VTC
locations that are centrally managed.
SC-15(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined online
meetings and teleconferences]
All VTC and all IP based online meetings and
conferences (excludes audio only teleconferences
using traditional telephony).
SC-17
[Assignment: organization-defined certificate
policy]
The certificate policy defined in CNSSP No. 25.
SC-18(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined mobile code
requirements]
The following requirements:
(a) Emerging mobile code technologies that have
not undergone a risk assessment and been
assigned to a Risk Category by the CIO are not
used.
(b) Category 1 mobile code is signed with a code
signing certificate; use of unsigned Category 1
mobile code is prohibited; use of Category 1
mobile code technologies that cannot block or
disable unsigned mobile code (e.g., Windows
Scripting Host) is prohibited.
(c) Category 2 mobile code which executes in a
constrained environment without access to
system resources (e.g., Windows registry, file
system, system parameters, and network
connections to other than the originating host)
may be used.
(d) Category 2 mobile code that does not execute
in a constrained environment may be used when
obtained from a trusted source over an assured
channel (e.g., SIPRNet, SSL connection,
S/MIME, code is signed with an approved code
signing certificate).
(e) Category 3 (mobile code having limited

CNSSI No. 1253
E-17
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
functionality, with no capability for unmediated
access to the services and resources of a
computing platform) mobile code may be used.
SC-18(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined unacceptable
mobile code]
All unacceptable mobile code such as:
(a) Emerging mobile code technologies that have
not undergone a risk assessment and been
assigned to a Risk Category by the CIO.
(b) unsigned Category 1 mobile code and
Category 1 mobile code technologies that cannot
block or disable unsigned mobile code (e.g.,
Windows Scripting Host).
(d) Category 2 mobile code not obtained from a
trusted source over an assured channel (e.g.,
SIPRNet, SSL connection, S/MIME, code is
signed with an approved code signing
certificate).
SC-18(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined software
applications]
[Assignment: organization-defined actions]
Software applications and such as but not limited
to email, scriptable document/file editing
applications that support documents with
embedded code (e.g., MS Office
applications/documents), etc.
Prompting the user for permission.
SC-24
[Assignment: organization-defined known-state]
[Assignment: organization-defined types of
failures]
[Assignment: organization-defined system state
information]
Known secure state.
All types of failures.
Information necessary to determine cause of
failure and to return to operations with least
disruption to mission/business processes.
SC-28
[Selection (one or more): confidentiality;
integrity]
Assignment: organization-defined information at
rest]
Confidentiality and integrity.
All information not cleared for public release.
SC-28(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined information]
[Assignment: organization-defined information
system components]
All information not cleared for public release.
System components outside of organization
facilities.
SC-43
a. [Assignment: organization-defined
information system components]
All information system components (through the
use of an acceptable use agreement).
SI-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
a. All personnel.
b.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
b.1. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b.2. [Assignment: organization-defined
b.2. At least annually if not otherwise defined in

CNSSI No. 1253
E-18
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
frequency]
formal organizational policy.
SI-2
c. [Assignment: organization-defined time
period]
c. 30 days if not otherwise defined in formal
organizational policy.
SI-2(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least once a quarter.
SI-2(6)
[Assignment: organization-defined software and
firmware components]
All upgraded/replaced software and firmware
components that are no longer required for
operation when possible.
SI-3
c.1. [Assignment: organization-defined
frequency]
[Selection (one or more); endpoint; network
entry/exit points]
c.1. At least weekly.
Endpoints and network entry/exit points.
2. [Selection (one or more): block malicious
code; quarantine malicious code; send alert to
administrator;
[Assignment: organization-defined action]]
c2. Block and quarantine malicious code then
send an alert to the system administrator.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
SI-3(8)
[Assignment: organization-defined unauthorized
operating system commands]
[Assignment: organization-defined information
system hardware components]
[Selection (one or more): issues a warning;
audits the command execution; prevents the
execution of the command]
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Audits the command execution and prevents the
execution of the command.
SI-4(4)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
Continuously.
SI-4(9)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least monthly.
SI-5
a. [Assignment: organization-defined external
organizations]
a. Minimally the US-CERT.
c. [Selection (one or more): [Assignment:
organization-defined personnel or roles]
[Assignment: organization-defined elements
within the organization]
[Assignment: organization-defined external
organizations]]
c. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
SI-6
a. [Assignment: organization-defined security
functions]
a. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
b. [Selection (one or more):
[Assignment: organization-defined system
transitional states]; upon command by user with
appropriate privilege
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]];
b. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for

CNSSI No. 1253
E-19
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
all NSS.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined personnel
or roles]
c. Minimally notifies system/security
administrator.
d. [Selection (one or more): shuts the
information system down; restarts the
information system
[Assignment: organization-defined alternative
action(s)]
d. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level
for all NSS.
Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
SI-6(3)
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel or
roles].
Responsible security personnel (e.g., AO, SISO,
ISSO, ISSM, etc.).
SI-7(9)
[Assignment: organization-defined devices]
All devices capable of verification of the boot
process.
SI-7(13)
[Assignment: organization-defined personnel or
roles]
Authorizing Official.
SI-7(15)
[Assignment: organization-defined software or
firmware components]
All software and firmware from vendors/sources
that provide cryptographic mechanisms to enable
the validation of code authenticity and integrity.
SI-10
[Assignment: organization-defined information
inputs]
All inputs to web/application servers, database
servers, and any system or application input that
might receive a crafted exploit toward executing
some code or buffer overflow.
PM-1
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually if not otherwise defined
informal organizational policy.
PM-9
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined
informal organizational policy.
NIST SP 800-53 Rev4, Appendix J, Privacy Control Catalog
AR-1
c. [Assignment: organization-defined allocation
of budget and staffing]
c. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
f. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency,
at least biennially]
f. At least biennially if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
AR-4
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
Continuously.
AR-5
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency,
at least annually]
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency, at
least annually]
b. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency,
at least annually]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
DI-1
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least every 180 days if not otherwise defined
in formal organizational policy.
DI-1(2)
[Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
At least every 180 days if not otherwise defined
in formal organizational policy.
DM-1
c. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency,
at least annually]
c. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
DM-2
a. [Assignment: organization-defined time
a. In accordance with National Archives and

CNSSI No. 1253
E-20
ID
Control Text
Defined Value for NSS
period]
Records Administration (NARA).
c. [Assignment: organization-defined techniques
or methods]
c. Not appropriate to define at the CNSS level for
all NSS.
IP-4(1)
[Assignment: organization-defined time period]
2 business days.
SE-1
a. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
a. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.
b. [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]
b. At least annually if not otherwise defined in
formal organizational policy.

CNSSI No. 1253
F-1
APPENDIX F
OVERLAYS
GUIDANCE FOR SPECIAL CONDITIONS AND COMMUNITY-WIDE USE
Overlays are a specification of security controls, control enhancements, supplemental guidance,
and other supporting information intended to complement (and further refine) security control
baselines resulting in the initial security control set. CNSS uses overlays to build consensus
across communities of interest and identify relevant security controls that have broad-based
support for very specific circumstances, situations, and/or conditions that differ from the
assumptions in Section 2.1. Each overlay provides guidance to determine when it is applicable.
An overlay provides security control specifications that are directly applicable to its subject
matter.
11
Governance and Publication of Overlays
CNSS reviews and publishes all overlays that will be attachments to CNSSI No. 1253 Appendix
F. CNSS may also be involved in the development of such overlays.
The CNSS Safeguarding Working Group (SWG) manages the overlay initiation, development,
approval, publication, and maintenance processes. As new overlays are published or existing
overlays are revised, this appendix will be administratively updated. CNSS provides
downloadable copies of the approved and published overlays,
12
as well as the template to be used
in overlay development (see Attachment 1) and overlay development guidance. Overlays
marked “Unclassified//For Official Use Only” (UNCLASSIFIED//FOUO) are available on the
restricted CNSS website.
Attachments to Appendix F (Formerly Appendix K): CNSS Published Overlays
Attachment 1: Overlay Template (1 Aug 13)
Attachment 2: Space Platform Overlay (6 Jun 13)
Attachment 3: Cross Domain Solution Overlay (27 Sep 13)
Attachment 4: Intelligence Overlay (23 Oct 12) (Document is U//FOUO)
Attachment 5: Classified Information Overlay (9 May 14)
Attachment 6: Privacy Overlay (20 Apr 15)
11
Overlays are baseline independent; therefore, they do not consider whether or not a control is selected for any particular
baseline. In applying overlays in conjunction with a selected baseline, there may be many “duplicate” controls. These controls
do not have to be implemented twice; however, an overlay provides additional specifications relevant to its subject matter and a
justification for the tailoring process.
12
Overlays are published on the CNSS website with the CNSS Instructions, at: https://www.cnss.gov.
